Targeting Neuroimmune Interactions in Diabetic Neuropathy with Nanomedicine
- PMID: 34416821
- PMCID: PMC8823248
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2021.0123
Targeting Neuroimmune Interactions in Diabetic Neuropathy with Nanomedicine
Abstract
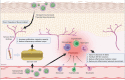
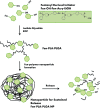
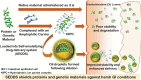
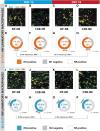
Significance: Diabetes is a major source of neuropathy and neuropathic pain that is set to continue growing in prevalence. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) and pain associated with diabetes are not adequately managed by current treatment regimens. Perhaps the greatest difficulty in treating DPN is the complex pathophysiology, which involves aspects of metabolic disruption and neurotrophic deficits, along with neuroimmune interactions. There is, therefore, an urgent need to pursue novel therapeutic options targeting the key cellular and molecular players. Recent Advances: To that end, cellular targeting becomes an increasingly compelling drug delivery option as our knowledge of neuroimmune interactions continues to mount. These nanomedicine-based approaches afford a potentially unparalleled specificity and longevity of drug targeting, using novel or established compounds, all while minimizing off-target effects. Critical Issues: The DPN therapeutics directly targeted at the nervous system make up the bulk of currently available treatment options. However, there are significant opportunities based on the targeting of non-neuronal cells and neuroimmune interactions in DPN. Future Directions: Nanomedicine-based agents represent an exciting opportunity for the treatment of DPN with the goals of improving the efficacy and safety profile of analgesia, as well as restoring peripheral neuroregenerative capacity. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 36, 122-143.
Keywords: diabetes; diabetic neuropathy; nanomedicine; neuroimmune interaction; neuropathy; pain.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- AboulFotouh K, Allam AA, El-Badry M, and El-Sayed AM. Role of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems in optimizing the oral delivery of hydrophilic macromolecules and reducing interindividual variability. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 167: 82–92, 2018. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar A, Andleeb A, Waris TS, Bazzar M, Moradi AR, Awan NR, and Yar M. Neurodegenerative diseases and effective drug delivery: a review of challenges and novel therapeutics. J Control Release 330: 1152–1167, 2021. - PubMed
-
- Alvarado-Vazquez PA, Bernal L, Paige CA, Grosick RL, Moracho Vilrriales C, Ferreira DW, Ulecia-Moron C, and Romero-Sandoval EA. Macrophage-specific nanotechnology-driven CD163 overexpression in human macrophages results in an M2 phenotype under inflammatory conditions. Immunobiology 222: 900–912, 2017. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alvarado-Vazquez PA, Grosick RL, Moracho-Vilrriales C, Ward E, Threatt T, and Romero-Sandoval EA. Cytokine production capabilities of human primary monocyte-derived macrophages from patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 with and without diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Pain Res 12: 69–81, 2019. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

