Identification of circRNA-Interacting Proteins by Affinity Pulldown
- PMID: 34417753
- PMCID: PMC8501521
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1697-0_17
Identification of circRNA-Interacting Proteins by Affinity Pulldown
Abstract
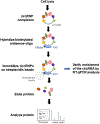
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) comprise a vast class of covalently closed transcripts, generated primarily via backsplicing. Most circRNAs arise from full or partial exons, but they can also arise from introns, and from combinations of introns and exons. While high-throughput RNA-sequencing analysis has identified tens of thousands of circRNAs expressed in different tissues and growth conditions, the function of circRNAs has only been described for a handful of them. As most circRNAs appear not to encode peptides, their function is presumed to be linked to their interaction with a range of molecules, particularly other nucleic acids (notably microRNAs) and proteins. A major impediment to identifying circRNA-associated molecules is a lack of suitable methodologies capable of analyzing specifically circRNAs and not their linear RNA counterparts with which they share most of their sequence. Here, we describe a flexible and robust method for identifying the proteins that associate with a given circRNA. The affinity pulldown assay is based on the use of a biotinylated antisense oligomer that recognizes the circRNA-specific junction sequence. Following pulldown using streptavidin beads, the proteins are eluted from the circRNP (circribonucleoprotein) complex and identified by mass spectroscopy; validation by Western blot analysis and other methods would then confirm the identity of the circRNA-associated proteins. We present a detailed step-by-step protocol, tips to optimize the analysis, troubleshooting suggestions, and assistance in interpreting the results. In sum, this protocol enables the discovery of proteins present in circRNPs, a critical effort toward elucidating circRNA function.
Keywords: Antisense oligomer; Backsplice junction; Ribonucleoprotein complex; circRNA-Protein; circRNAs.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

