Relevance of well-being, resilience, and health-related quality of life to mental health profiles of European adolescents: results from a cross-sectional analysis of the school-based multinational UPRIGHT project
- PMID: 34417859
- PMCID: PMC8379563
- DOI: 10.1007/s00127-021-02156-z
Relevance of well-being, resilience, and health-related quality of life to mental health profiles of European adolescents: results from a cross-sectional analysis of the school-based multinational UPRIGHT project
Abstract
Purpose: The existing evidence suggests that a complete evaluation of mental health should incorporate both psychopathology and mental well-being indicators. However, few studies categorize European adolescents into subgroups based on such complete mental health data. This study used the data on mental well-being and symptoms of mental and behavioral disorders to explore the mental health profiles of adolescents in Europe.
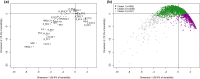
Methods: Data collected from adolescents (N = 3767; mean age 12.4 [SD = 0.9]) from five European countries supplied the information on their mental well-being (personal resilience, school resilience, quality of life, and mental well-being) and mental and behavioral disorder symptoms (anxiety, depression, stress, bullying, cyber-bullying, and use of tobacco, alcohol, or cannabis). Multiple correspondence analysis and cluster analysis were combined to classify the youths into mental health profiles.
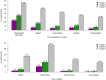
Results: Adolescents were categorized into three mental health profiles. The "poor mental health" profile (6%) was characterized by low levels of well-being and moderate symptoms of mental disorders. The "good mental health" profile group (26%) showed high well-being and few symptoms of mental disorders, and the "intermediate mental health" profile (68%) was characterized by average well-being and mild-to-moderate symptoms of mental disorders. Groups with higher levels of well-being and fewer symptoms of mental disorders showed lower rates of behavioral problems. Mental well-being indicators strongly contributed to this classification.
Conclusion: Adolescents with the "intermediate" or "poor" mental health profiles may benefit from interventions to improve mental health. Implications for school-based interventions are discussed.
Trial registration number (trn) and date of registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03951376. Registered 15 May 2019.
Keywords: Mental disorders; Mental health promotion; Prevention; School interventions; Well-being; Youth.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Suldo SM, Shaffer EJ. Looking beyond psychopathology: the dual-factor model of mental health in youth. School Psychol Rev. 2008;37(1):52–68. doi: 10.1080/02796015.2008.12087908. - DOI
-
- World Health Organisation (2019) Mental health: Fact sheet. https://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0004/404851/MNH_FactShee.... Accessed 04 Oct 2020
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

