Efficacy and safety of arimoclomol in Niemann-Pick disease type C: Results from a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, multinational phase 2/3 trial of a novel treatment
- PMID: 34418116
- PMCID: PMC9293014
- DOI: 10.1002/jimd.12428
Efficacy and safety of arimoclomol in Niemann-Pick disease type C: Results from a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, multinational phase 2/3 trial of a novel treatment
Abstract
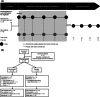
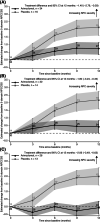
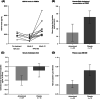
Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC) is a rare, genetic, progressive neurodegenerative disorder with high unmet medical need. We investigated the safety and efficacy of arimoclomol, which amplifies the heat shock response to target NPC protein misfolding and improve lysosomal function, in patients with NPC. In a 12-month, prospective, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2/3 trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02612129), patients (2-18 years) were randomised 2:1 to arimoclomol:placebo, stratified by miglustat use. Routine clinical care was maintained. Arimoclomol was administered orally three times daily. The primary endpoint was change in 5-domain NPC Clinical Severity Scale (NPCCSS) score from baseline to 12 months. Fifty patients enrolled; 42 completed. At month 12, the mean progression from baseline in the 5-domain NPCCSS was 0.76 with arimoclomol vs 2.15 with placebo. A statistically significant treatment difference in favour of arimoclomol of -1.40 (95% confidence interval: -2.76, -0.03; P = .046) was observed, corresponding to a 65% reduction in annual disease progression. In the prespecified subgroup of patients receiving miglustat as routine care, arimoclomol resulted in stabilisation of disease severity over 12 months with a treatment difference of -2.06 in favour of arimoclomol (P = .006). Adverse events occurred in 30/34 patients (88.2%) receiving arimoclomol and 12/16 (75.0%) receiving placebo. Fewer patients had serious adverse events with arimoclomol (5/34, 14.7%) vs placebo (5/16, 31.3%). Treatment-related serious adverse events (n = 2) included urticaria and angioedema. Arimoclomol provided a significant and clinically meaningful treatment effect in NPC and was well tolerated.
Keywords: NPC clinical severity scale; Niemann-Pick disease type C; arimoclomol; biomarker; double-blindplacebo-controlled; heat shock protein.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of SSIEM.
Conflict of interest statement
Eugen Mengel has received investigator fees and consultant honoraria from Actelion, Alexion, Orphazyme A/S, Sanofi Genzyme, and Takeda. Marc C. Patterson has received, or will receive, research support from Actelion, Amicus, Glycomine, NIH, Orphazyme A/S, and Shire/Takeda; has served as Chair of the Scientific Advisory Committee of a Registry of Niemann‐Pick disease type C, sponsored by Actelion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; has received consultancy fees from Amicus, Genzyme, IntraBio, Novartis, Orphazyme A/S, Takeda, and Vtesse‐Sucampo‐Mallinckrodt; holds stock in IntraBio; and receives a stipend as Editor‐in Chief of the
Figures
References
-
- Lloyd‐Evans E, Platt FM. Lipids on trial: the search for the offending metabolite in Niemann‐Pick type C disease. Traffic. 2010;11:419‐428. - PubMed

