Sweet Electronics: Honey-Gated Complementary Organic Transistors and Circuits Operating in Air
- PMID: 34418204
- PMCID: PMC11468742
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.202103183
Sweet Electronics: Honey-Gated Complementary Organic Transistors and Circuits Operating in Air
Abstract
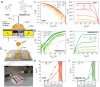
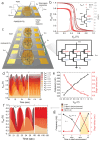
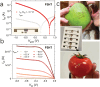
Sustainable harnessing of natural resources is key moving toward a new-generation electronics, which features a unique combination of electronic functionality, low cost, and absence of environmental and health hazards. Within this framework, edible electronics, of which transistors and circuits are a fundamental component, is an emerging field, exploiting edible materials that can be safely ingested, and subsequently digested after performing their function. Dielectrics are a critical functional element of transistors, often constituting their major volume. Yet, to date, there are only scarce examples of electrolytic food-based materials able to provide low-voltage operation of transistors at ambient conditions. In this context, a cost-effective and edible substance, honey, is proposed to be used as an electrolytic gate viscous dielectric in electrolyte-gated organic field-effect transistors (OFETs). Both n- and p-type honey-gated OFETs (HGOFETs) are demonstrated, with distinctive features such as low voltage (<1 V) operation, long-term shelf life and operation stability in air, and compatibility with large-area fabrication processes, such as inkjet printing on edible tattoo-paper. Such complementary devices enable robust honey-based integrated logic circuits, here exemplified by inverting logic gates and ring oscillators. A marked device responsivity to humidity provides promising opportunities for sensing applications, specifically, for moisture control of dried or dehydrated food.
Keywords: edible electronics; electrolyte-gated transistors; honey; organic electronics; printed electronics.
© 2021 The Authors. Advanced Materials published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Irimia‐Vladu M., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 588. - PubMed
-
- Mihai Irimia‐Vladu S. B., Glowacki E. D., Sariciftci N. S., Green Materials for Electronics, Wiley‐VCH, Weinheim, Germany: 2018.
-
- Li W., Liu Q., Zhang Y., Li C., He Z., Choy W. C. H., Low P. J., Sonar P., Kyaw A. K. K., Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001591. - PubMed
-
- Steiger C., Abramson A., Nadeau P., Chandrakasan A. P., Langer R., Traverso G., Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 83.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

