COVID-19 severity and outcome in multiple sclerosis: Results of a national, registry-based, matched cohort study
- PMID: 34418735
- PMCID: PMC8366056
- DOI: 10.1016/j.msard.2021.103217
COVID-19 severity and outcome in multiple sclerosis: Results of a national, registry-based, matched cohort study
Abstract
Background: Risk factors associated with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) have been described. Recent improvements in supportive care measures and increased testing capacity may modify the risk of severe COVID-19 outcome in MS patients. This retrospective study evaluates the severity and outcome of COVID-19 in MS and characterizes temporal trends over the course of the pandemic in the United States.
Methods: We conducted a comparative cohort study using de-identified electronic health record (EHR) claims-based data. MS patients diagnosed with COVID-19 between February 2, 2020 and October 13, 2020 were matched (1:2) to a control group using propensity score analysis. The primary outcome was a composite of intensive care unit (ICU) admission, mechanical ventilation, and/or death.
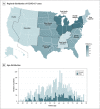
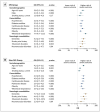
Results: A total of 2,529 patients (843 MS and 1,686 matched controls) were included. Non-ambulatory and pre-existing comorbidities were independent risk factors for COVID-19 severity. The risk for the severe composite outcome was lower in the late cohorts compared with the early cohorts.
Conclusions: The majority of MS patients actively treated with a disease-modifying therapy (DMT) had mild disease. The observed trend toward a reduction in severity risk in recent months suggests an improvement in COVID-19 outcome.
Keywords: COVID-19; Disease-modifying therapy; Multiple sclerosis; Outcome; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

