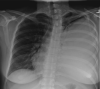
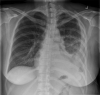
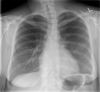
The use of fibrinolytic therapy for parapneumonic effusion in pregnancy: a case report and a review
- PMID: 34419110
- PMCID: PMC8379832
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-021-01619-3
The use of fibrinolytic therapy for parapneumonic effusion in pregnancy: a case report and a review
Abstract
The use of intrapleural fibrinolytics for complicated parapneumonic effusion has been shown to be an effective and safe alternative to surgery. However, there is limited evidence about its use during pregnancy. We present a case and a review of the literature of pregnant women who had successful treatment of their complicated parapneumonic effusion with intrapleural fibrinolytics. To our knowledge this is the first review of cases of pregnant women with parapneumonic effusion managed with intrapleural fibrinolytic.
Keywords: Fibrinolytics; Parapneumonic effusion; Pregnancy.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Charlie Strange. Management and prognosis of parapneumonic pleural effusion and empyema in adults—UpToDate. 2021 [cited 2021 Mar 15].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources