Pericytic porters: helping leptin step in
- PMID: 34420855
- PMCID: PMC8764624
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2021.08.001
Pericytic porters: helping leptin step in
Abstract
A new mechanism of leptin extravasation from the bloodstream into the brain may have been discovered. According to recent findings by Butiaeva et al., pericytes within the blood-brain barrier (BBB) express the leptin receptor and, upon activation, facilitate the movement of the appetite-suppressing hormone into deeper regions of the hypothalamus.
Keywords: blood–brain barrier; hypothalamus; leptin; obesity; pericyte.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
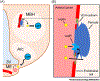
Comment on
-
Leptin receptor-expressing pericytes mediate access of hypothalamic feeding centers to circulating leptin.Cell Metab. 2021 Jul 6;33(7):1433-1448.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.05.017. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Cell Metab. 2021. PMID: 34129812
References
-
- Friedman JM (2019) Leptin and the endocrine control of energy balance. Nat. Metab 1, 754–764 - PubMed
-
- Butiaeva LI et al. (2021) Leptin receptor-expressing pericytes mediate access of hypothalamic feeding centers to circulating leptin. Cell Metab. 33, 1433–1448 - PubMed
-
- Burguera B et al. (2000) Obesity is associated with a decreased leptin transport across the blood–brain barrier in rats. Diabetes 49, 1219–1223 - PubMed
-
- Munzberg H and Myers MG Jr. (2005) Molecular and anatomical determinants of central leptin resistance. Nat. Neurosci 8, 566–570 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

