Multi-Clinic Quality Improvement Initiative Increases Continuous Glucose Monitoring Use Among Adolescents and Young Adults With Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 34421201
- PMCID: PMC8329017
- DOI: 10.2337/cd21-0026
Multi-Clinic Quality Improvement Initiative Increases Continuous Glucose Monitoring Use Among Adolescents and Young Adults With Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
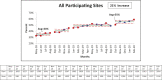
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) use is associated with improved A1C outcomes and quality of life in adolescents and young adults with diabetes; however, CGM uptake is low. This article reports on a quality improvement (QI) initiative of the T1D Exchange Quality Improvement Collaborative to increase CGM use among patients in this age-group. Ten centers participated in developing a key driver diagram and center-specific interventions that resulted in an increase in CGM use from 34 to 55% in adolescents and young adults over 19-22 months. Sites that performed QI tests of change and documented their interventions had the highest increases in CGM uptake, demonstrating that QI methodology and sharing of learnings can increase CGM uptake.
© 2021 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
O.E. is a compensated Health Equity Advisory Board member for Medtronic Diabetes and serves as principal investigator for investigator-led projects sponsored by Abbott, Eli Lilly, Insulet, and Medtronic. M.C. has consulting arrangements with Eli Lilly and Medtronic, is an employee (chief medical officer) of Glooko, and has received research support from Abbott Diabetes Care and Dexcom and travel support from Intrexon and Provention Bio. J.M.L. is on a medical advisory board for GoodRx. D.M.M. has received research support from the Helmsley Charitable Trust, JDRF, the National Institutes of Health, and the National Science Foundation; his institution has received research support from Bigfoot Biomedical, Dexcom, Insulet, Medtronic, Roche, and Tandem; and he has been a consultant for Abbott, Aditxt, Dompe, Eli Lilly, the Helmsley Charitable Trust, Insulet, Medtronic, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures

References
-
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group; Nathan DM, Genuth S, Lachin J, et al. . The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;329:977–986 - PubMed
-
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group . Effect of intensive diabetes treatment on the development and progression of long-term complications in adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. J Pediatr 1994;125:177–188 - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association . 13. Children and adolescents: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2020. Diabetes Care 2020;43(Suppl. 1):S163–S182 - PubMed
-
- Miller KM, Foster NC, Beck RW, et al. .; T1D Exchange Clinic Network . Current state of type 1 diabetes treatment in the U.S.: updated data from the T1D Exchange clinic registry. Diabetes Care 2015;38:971–978 - PubMed

