Update on Non-neuraxial Labor Analgesia
- PMID: 34421391
- PMCID: PMC8371034
- DOI: 10.1007/s40140-021-00463-4
Update on Non-neuraxial Labor Analgesia
Abstract
Purpose of review: This review will present recent updates for the use of non-neuraxial analgesia for laboring women.
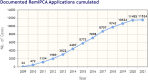
Recent findings: Non-neuraxial labor analgesia by nitrous oxide and intravenous opioids are described, and safety concerns with regard to remifentanil administration have been a major focus of recent studies. Fentanyl and nitrous oxide offer some efficacy, albeit less than remifentanil, however with a greater safety margin.
Summary: Women may request or require alternatives to neuraxial labor analgesia, in some cases due to concurrent comorbidities. Remifentanil offers the most efficacious alternative analgesia option; however, safety concerns may preclude widespread use.
Keywords: Analgesia; Epidural; Labor; Non-neuraxial; Remifentanil; Safety.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestThe authors do not have any potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Souza MAC, Guida JG, Souza JP, Gulmezoglu JP, Betran AM, A P. WHO-MCS study group: Analgesia for vaginal birth: secondary analysis from the WHO Multicountry Survey on Maternal and Newborn Health. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics. 2021;152(3):401–408. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.13424. - DOI - PubMed
-
- SLM L, Vink ML, Godfried MB, Beenakkers ICM, Schellevis FG, Mol BW, Verhoeven CJ. Serious adverse events attributed to remifentanil patient-controlled analgesia during labor in The Netherlands. International journal of obstetric anesthesia. 2019;39:22–28. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
