The Challenges of Crizotinib Treatment in a Child With Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
- PMID: 34421417
- PMCID: PMC8372857
- DOI: 10.5863/1551-6776-26.6.647
The Challenges of Crizotinib Treatment in a Child With Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
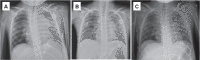
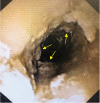
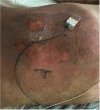
Survival in cases involving childhood malignancy is reaching nearly 80% in high-income countries, yet cancer remains one of the leading disease-related causes of death in children. In adult oncology the role of targeted therapies is established, but information regarding the use of these therapies in children is limited, largely because targeted therapies were developed in the context of adult pathologies. The few pediatric reports regarding crizotinib, an anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitor, seem promising. This case of an 8-year-old male with an ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma highlights the challenges of treating children with crizotinib. Our experience with crizotinib was more challenging than described in the limited pediatric reports. Not only was the tumor response poorer than described in the reports, but a substantial amount of side-effects and practical difficulties, such as the method of administration and dosing, made management challenging. Many challenges for the use of targeted therapy in pediatric care currently persist. The limited research in pediatric populations leaves uncertainty regarding efficacy and short- and long-term side effects as well as practical difficulties. Despite a clear underlying biological rationale for certain targeted therapies, their contribution toward improving the outcome of childhood cancer remains largely unclear.
Keywords: anaplastic large cell lymphoma; crizotinib; molecular targeted therapy; off-label use; oncology; pediatrics.
Copyright. Pediatric Pharmacy Association. All rights reserved. For permissions, email: mhelms@pediatricpharmacy.org 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures. The authors declare no conflicts or financial interest in any product or service mentioned in the manuscript, including grants, equipment, medications, employment, gifts, and honoraria. The authors had full access to all patient information in this report and take responsibility for the integrity and accuracy of the report.
Figures

References
-
- Guillaume-Czitrom S. Biologic targeted therapies in pediatric rheumatology. Joint Bone Spine. 2014;81(suppl 1):2–48. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
