Auditory Disturbances and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Brain Inflammation or Cochlear Affection? Systematic Review and Discussion of Potential Pathogenesis
- PMID: 34421805
- PMCID: PMC8373381
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.707207
Auditory Disturbances and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Brain Inflammation or Cochlear Affection? Systematic Review and Discussion of Potential Pathogenesis
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Auditory disturbances and SARS-CoV-2 infection: brain inflammation or cochlear affection? Systematic review and discussion of potential pathogenesis.Front Neurol. 2023 Jun 26;14:1234744. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1234744. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37435158 Free PMC article.
Abstract
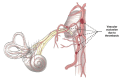
Patients affected by COVID-19 present a series of different symptoms; despite some of these are common, other less likely appear. Auditory symptoms seem to be less frequent, maybe because rarer or, alternatively, because they are underestimated during the clinical investigation. The hearing impairment might be related to the central or peripheral involvement of the auditory pathways; in particular, the likelihood of thrombosis might be one of the causes. To date, the prevalence of auditory symptoms such as sudden or progressive sensorineural hearing loss and tinnitus is unclear in COVID-19 patients. However, their presence might be an early sign of thrombosis or spread of the infection into the brain. In this systematic review of the literature we investigated the presence of auditory symptoms in COVID-19 patients and discussed their potential origin and causal relationship with SARS-CoV-2. Results showed that, despite rarely, auditory impairment can appear in patients with COVID-19 and should always be investigated for an early treatment and potential indicator of involvement of the central nervous system.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; brain inflammation; hearing loss; sudden hearing impairment; tinnitus.
Copyright © 2021 De Luca, Scarpa, Ralli, Tassone, Simone, De Campora, Cassandro and Di Stadio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer AF declared a past co-authorship with two of the authors AS and CC to the handling Editor.
Figures

References
-
- De Luca P, Scarpa A, Ralli M, De Vincentiis M, Cassandro E, Chiarella G, et al. . Nasal, pharyngeal and laryngeal endoscopy procedures during COVID-19 pandemic: available recommendations from national and international societies. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. (2020) 277:2151–3. 10.1007/s00405-020-06028-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

