A comparative study of the RuiBreath and NIOX VERO analyzers for detecting fractional exhaled nitric oxide
- PMID: 34422368
- PMCID: PMC8339745
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-21-25
A comparative study of the RuiBreath and NIOX VERO analyzers for detecting fractional exhaled nitric oxide
Abstract
Background: Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) measurement is a reliable, noninvasive marker of airway inflammation. Portable FeNO analyzers facilitate the assessment of airway inflammation in primary care. Differences between analyzers from different manufacturers are not comparable. Here, we aimed to compare the FeNO values obtained by a new portable device (RuiBreath, Guangzhou Ruipu Medical Technology Co., Ltd, Guangzhou, China) to those obtained by the widely used NIOX VERO portable analyzer (Aerocrine AB, Solna, Sweden) in patients with asthma.
Methods: This prospective validation study enrolled patients (≥14 years old) with asthma over a 2-month period (July and August 2019) at the Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital. At least one valid FeNO measurement was obtained using each analyzer for all the participants.
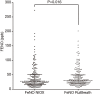
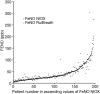
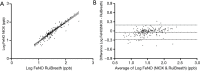
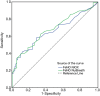
Results: There were 197 participants in this study. The FeNONIOX and FeNORuiBreath values significantly differed (P=0.016). After log-transformation, a difference was found only when the FeNONIOX was <25 ppb (P<0.001). The FeNONIOX and FeNORuiBreath values had a significant correlation (r=0.938, P<0.001), which was confirmed by the Altman-Bland plot. Using a receiver-operating characteristic curve analysis, when using 49 ppb as the cut-off point for the two devices in identifying patients with symptomatic asthma symptoms, the sensitivity and specificity were 0.42 and 0.88, respectively, by NIOX, and 0.40 and 0.89, respectively, by RuiBreath.
Conclusions: This is the first report of FeNO values obtained by the new portable RuiBreath FeNO analyzer. The FeNORuiBreath values are reliable and directly comparable with the FeNONIOX values.
Keywords: Exhaled nitric oxide; NIOX VERO; RuiBreath; airway inflammation; asthma.
2021 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://dx.doi.org/10.21037/jtd-21-25). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Difference between two exhaled nitric oxide analyzers, NIOX VERO® electrochemical hand-held analyzer and NOA280i® chemiluminescence stationary analyzer.J Asthma. 2019 Feb;56(2):167-172. doi: 10.1080/02770903.2018.1439953. Epub 2018 Oct 18. J Asthma. 2019. PMID: 30335533
-
Measurement of fractional exhaled nitric oxide by a new portable device: comparison with the standard technique.J Asthma. 2010 Sep;47(7):805-9. doi: 10.3109/02770903.2010.485667. J Asthma. 2010. PMID: 20670207
-
Comparison of fractional exhaled nitric oxide levels measured by different analyzers produced by different manufacturers.J Asthma. 2020 Nov;57(11):1216-1226. doi: 10.1080/02770903.2019.1642351. Epub 2019 Jul 22. J Asthma. 2020. PMID: 31288573
-
Measurement of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide in Adults: Comparison of Two Different Analyzers (NIOX VERO and NObreath).Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2021 Jul;84(3):182-187. doi: 10.4046/trd.2020.0137. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2021. PMID: 33691356 Free PMC article.
-
[Exhaled nitric oxide in children: a noninvasive marker of airway inflammation].Arch Bronconeumol. 2008 Jan;44(1):41-51. doi: 10.1016/s1579-2129(08)60007-5. Arch Bronconeumol. 2008. PMID: 18221726 Review. Spanish.
References
-
- British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (BTS/SIGN) national clinical guideline on management of asthma (SIGN158). London: British Thoracic Society, 2019.
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) global strategy for asthma management and prevention. Fontana: Global Initiative for Asthma, 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
