A Root in Synapsis and the Other One in the Gut Microbiome-Brain Axis: Are the Two Poles of Ketogenic Diet Enough to Challenge Glioblastoma?
- PMID: 34422883
- PMCID: PMC8378133
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2021.703392
A Root in Synapsis and the Other One in the Gut Microbiome-Brain Axis: Are the Two Poles of Ketogenic Diet Enough to Challenge Glioblastoma?
Abstract
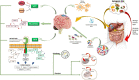
Glioblastoma is the most frequent and aggressive brain cancer in adults. While precision medicine in oncology has produced remarkable progress in several malignancies, treatment of glioblastoma has still limited available options and a dismal prognosis. After first-line treatment with surgery followed by radiochemotherapy based on the 2005 STUPP trial, no significant therapeutic advancements have been registered. While waiting that genomic characterization moves from a prognostic/predictive value into therapeutic applications, practical and easy-to-use approaches are eagerly awaited. Medical reports on the role of the ketogenic diet in adult neurological disorders and in glioblastoma suggest that nutritional interventions may condition outcomes and be associated with standard therapies. The acceptable macronutrient distribution of daily calories in a regular diet are 45-65% of daily calories from carbohydrates, 20-35% from fats, and 10-35% from protein. Basically, the ketogenic diet follows an approach based on low carbohydrates/high fat intake. In carbohydrates starvation, body energy derives from fat storage which is used to produce ketones and act as glucose surrogates. The ketogenic diet has several effects: metabolic interference with glucose and insulin and IGF-1 pathways, influence on neurotransmission, reduction of oxidative stress and inflammation, direct effect on gene expression through epigenetic mechanisms. Apart from these central effects working at the synapsis level, recent evidence also suggests a role for microbiome and gut-brain axis induced by a ketogenic diet. This review focuses on rationales supporting the ketogenic diet and clinical studies will be reported, looking at future possible perspectives.
Keywords: glioblastoma; gut-brain axis; ketogenic diet; microbiota; warburg effect.
Copyright © 2021 Montella, Sarno, Altucci, Cioffi, Sigona, Di Colandrea, De Simone, Marinelli, Facchini, De Vita, Berretta, de Falco and Facchini.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJB, et al. European organisation for research and treatment of cancer brain tumor and radiotherapy groups; national cancer institute of canada clinical trials group. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. (2005) 352:987–96. 10.1056/NEJMoa043330 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lombardi MY, Assem M, De Vleeschouwer S. Chapter 1: Glioblastoma Genomics: a very complicated story. In: De Vleeschouwer S, editor. Glioblastoma. Brisbane, QLD: Codon Publications; (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous