Antibody Nanocarriers for Cancer Management
- PMID: 34423177
- PMCID: PMC8373047
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cobme.2021.100295
Antibody Nanocarriers for Cancer Management
Abstract
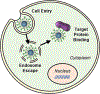
Antibodies are extremely valuable tools in modern medicine due to their ability to target diseased cells through selective antigen binding and thereby regulate cellular signaling or inhibit cell-cell interactions with high specificity. However, the therapeutic utility of freely delivered antibodies is limited by high production costs, low efficacy, dose-limiting toxicities, and inability to cross the cellular membrane (which hinders antibodies against intracellular targets). To overcome these limitations, researchers have begun to develop nanocarriers that can improve antibodies' delivery efficiency, safety profile, and clinical potential. This review summarizes recent advances in the design and implementation of nanocarriers for extracellular or intracellular antibody delivery, emphasizing important design considerations, and points to future directions for the field.
Keywords: binding affinity; multivalency; nanoparticles; signal cascade interference; targeted antibodies.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement Nothing to declare. Declaration of interests The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
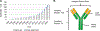
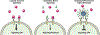

References
-
- Grilo AL, Mantalaris A: The Increasingly Human and Profitable Monoclonal Antibody Market. Trends Biotechnol 2019, 37:9–16. - PubMed
-
- Search of: mab | Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs. [Accessed March 17, 2021].
-
- Search of: monoclonal antibodies | Recruiting, Active, not recruiting Studies - List Results - ClinicalTrials.gov. [Accessed March 18, 2021].
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
