Systematic morphological and morphometric analysis of identified olfactory receptor neurons in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 34423777
- PMCID: PMC8410077
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.69896
Systematic morphological and morphometric analysis of identified olfactory receptor neurons in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
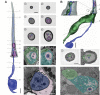
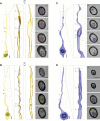
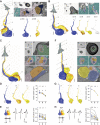
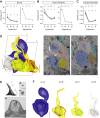
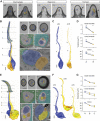
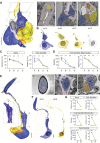
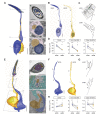
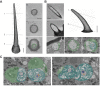
The biophysical properties of sensory neurons are influenced by their morphometric and morphological features, whose precise measurements require high-quality volume electron microscopy (EM). However, systematic surveys of nanoscale characteristics for identified neurons are scarce. Here, we characterize the morphology of Drosophila olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs) across the majority of genetically identified sensory hairs. By analyzing serial block-face electron microscopy images of cryofixed antennal tissues, we compile an extensive morphometric data set based on 122 reconstructed 3D models for 33 of the 40 identified antennal ORN types. Additionally, we observe multiple novel features-including extracellular vacuoles within sensillum lumen, intricate dendritic branching, mitochondria enrichment in select ORNs, novel sensillum types, and empty sensilla containing no neurons-which raise new questions pertinent to cell biology and sensory neurobiology. Our systematic survey is critical for future investigations into how the size and shape of sensory neurons influence their responses, sensitivity, and circuit function.
Keywords: 3D nanoscale model; D. melanogaster; antenna; morphometrics; neuroscience; olfactory receptor neuron; olfactory sensillum; serial block-face electron microscopy.
© 2021, Nava Gonzales et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CN, QM, EB, KC, RN, MM, ME, CS No competing interests declared
Figures









Similar articles
-
Asymmetric ephaptic inhibition between compartmentalized olfactory receptor neurons.Nat Commun. 2019 Apr 5;10(1):1560. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09346-z. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30952860 Free PMC article.
-
Sensillum-specific, topographic projection patterns of olfactory receptor neurons in the antennal lobe of the cockroach Periplaneta americana.J Comp Neurol. 2012 Jun 1;520(8):1687-701. doi: 10.1002/cne.23007. J Comp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22121009
-
Functional classification and central nervous projections of olfactory receptor neurons housed in antennal trichoid sensilla of female yellow fever mosquitoes, Aedes aegypti.Eur J Neurosci. 2007 Sep;26(6):1611-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05786.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17880395 Free PMC article.
-
Elements of olfactory reception in adult Drosophila melanogaster.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2013 Sep;296(9):1477-88. doi: 10.1002/ar.22747. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2013. PMID: 23904114 Review.
-
Early olfactory processing in Drosophila: mechanisms and principles.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2013 Jul 8;36:217-41. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-062111-150533. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23841839 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Drosophila olfaction: past, present and future.Proc Biol Sci. 2022 Dec 21;289(1989):20222054. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2022.2054. Epub 2022 Dec 14. Proc Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36515118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rehydration of Freeze Substituted Brain Tissue for Pre-embedding Immunoelectron Microscopy.Microsc Microanal. 2023 Sep 29;29(5):1694-1704. doi: 10.1093/micmic/ozad077. Microsc Microanal. 2023. PMID: 37584524 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral preprocessing in Drosophila facilitates odor classification.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 May 21;121(21):e2316799121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2316799121. Epub 2024 May 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38753511 Free PMC article.
-
An evolutionarily conserved cation channel tunes the sensitivity of gustatory neurons to ephaptic inhibition in Drosophila.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jan 21;122(3):e2413134122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2413134122. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 39823301 Free PMC article.
-
Innexin expression and localization in the Drosophila antenna indicate gap junction or hemichannel involvement in antennal chemosensory sensilla.Cell Tissue Res. 2024 Oct;398(1):35-62. doi: 10.1007/s00441-024-03909-3. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Cell Tissue Res. 2024. PMID: 39174822 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

