The Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 4 Inhibitor PF-06650833 Blocks Inflammation in Preclinical Models of Rheumatic Disease and in Humans Enrolled in a Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 34423919
- PMCID: PMC8671219
- DOI: 10.1002/art.41953
The Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 4 Inhibitor PF-06650833 Blocks Inflammation in Preclinical Models of Rheumatic Disease and in Humans Enrolled in a Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
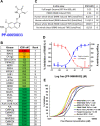
Objective: To investigate the role of PF-06650833, a highly potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor of interleukin-1-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4), in autoimmune pathophysiology in vitro, in vivo, and in the clinical setting.
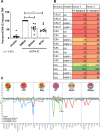
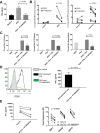
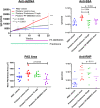
Methods: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) inflammatory pathophysiology was modeled in vitro through 1) stimulation of primary human macrophages with anti-citrullinated protein antibody immune complexes (ICs), 2) RA fibroblast-like synoviocyte (FLS) cultures stimulated with Toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands, as well as 3) additional human primary cell cocultures exposed to inflammatory stimuli. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) pathophysiology was simulated in human neutrophils, dendritic cells, B cells, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells stimulated with TLR ligands and SLE patient ICs. PF-06650833 was evaluated in vivo in the rat collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model and the mouse pristane-induced and MRL/lpr models of lupus. Finally, RNA sequencing data generated with whole blood samples from a phase I multiple-ascending-dose clinical trial of PF-06650833 were used to test in vivo human pharmacology.
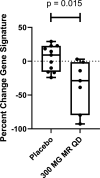
Results: In vitro, PF-06650833 inhibited human primary cell inflammatory responses to physiologically relevant stimuli generated with RA and SLE patient plasma. In vivo, PF-06650833 reduced circulating autoantibody levels in the pristane-induced and MRL/lpr murine models of lupus and protected against CIA in rats. In a phase I clinical trial (NCT02485769), PF-06650833 demonstrated in vivo pharmacologic action pertinent to SLE by reducing whole blood interferon gene signature expression in healthy volunteers.
Conclusion: These data demonstrate that inhibition of IRAK4 kinase activity can reduce levels of inflammation markers in humans and provide confidence in the rationale for clinical development of IRAK4 inhibitors for rheumatologic indications.
© 2021 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Targeting the Myddosome in Systemic Autoimmunity: Ready for Prime Time?Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Dec;73(12):2163-2165. doi: 10.1002/art.41951. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34424598 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
IRAK4 inhibitor attenuates inflammation.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021 Nov;17(11):646. doi: 10.1038/s41584-021-00699-8. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34584262 No abstract available.
References
-
- Malmström V, Catrina AI, Klareskog L. The immunopathogenesis of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: from triggering to targeting [review]. Nat Rev Immunol 2016;17:60–75. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Barton A, Burmester GR, Emery P, Firestein GS, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis [review]. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018;4:18001. - PubMed
-
- Aletaha D, Smolen JS. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis: a review. JAMA 2018;320:1360–72. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D. Rheumatoid arthritis therapy reappraisal: strategies, opportunities and challenges [review]. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2015;11:276–89. - PubMed
-
- Dörner T, Furie R. Novel paradigms in systemic lupus erythematosus [review]. Lancet 2019;393:2344–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

