Development and characterization of prototypes for in vitro and in vivo mouse models of ibrutinib-resistant CLL
- PMID: 34424317
- PMCID: PMC8405195
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003821
Development and characterization of prototypes for in vitro and in vivo mouse models of ibrutinib-resistant CLL
Abstract
Although ibrutinib improves the overall survival of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), some patients still develop resistance, most commonly through point mutations affecting cysteine residue 481 (C481) in Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTKC481S and BTKC481R). To enhance our understanding of the biological impact of these mutations, we established cell lines that overexpress wild-type or mutant BTK in in vitro and in vivo models that mimic ibrutinib-sensitive and -resistant CLL. MEC-1 cell lines stably overexpressing wild-type or mutant BTK were generated. All cell lines coexpressed GFP, were CD19+ and CD23+, and overexpressed BTK. Overexpression of wild-type or mutant BTK resulted in increased signaling, as evidenced by the induction of p-BTK, p-PLCγ2, and p-extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) levels, the latter further augmented upon IgM stimulation. In all cell lines, cell cycle profiles and levels of BTK expression were similar, but the RNA sequencing and reverse-phase protein array results revealed that the molecular transcript and protein profiles were distinct. To mimic aggressive CLL, we created xenograft mouse models by transplanting the generated cell lines into Rag2-/-γc-/- mice. Spleens, livers, bone marrow, and peripheral blood were collected. All mice developed CLL-like disease with systemic involvement (engraftment efficiency, 100%). We observed splenomegaly, accumulation of leukemic cells in the spleen and liver, and macroscopically evident necrosis. CD19+ cells accumulated in the spleen, bone marrow, and peripheral blood. The overall survival duration was slightly lower in mice expressing mutant BTK. Our cell lines and murine models mimicking ibrutinib-resistant CLL will serve as powerful tools to test reversible BTK inhibitors and novel, non-BTK-targeted therapeutics.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: V.G. has sponsored research agreements from Sunesis and Loxo Oncology. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



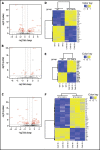

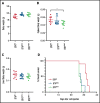
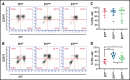
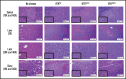

References
-
- Stevenson FK, Krysov S, Davies AJ, Steele AJ, Packham G.. B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2011;118(16): 4313-4320. - PubMed
-
- Bernal A, Pastore RD, Asgary Z, et al. . Survival of leukemic B cells promoted by engagement of the antigen receptor. Blood. 2001;98(10):3050-3057. - PubMed
-
- Howard DR, Munir T, McParland L, et al. . Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness results from the randomised, Phase IIB trial in previously untreated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia to compare fludarabine, cyclophosphamide and rituximab with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, mitoxantrone and low-dose rituximab: the attenuated dose rituximab with chemotherapy in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (ARCTIC) trial. Health Technol Assess. 2017;21(28):1-374. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

