Results of a randomized phase 3 study of oral sapacitabine in elderly patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (SEAMLESS)
- PMID: 34424530
- PMCID: PMC9523989
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.33828
Results of a randomized phase 3 study of oral sapacitabine in elderly patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (SEAMLESS)
Abstract
Background: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is fatal in elderly patients who are unfit for standard induction chemotherapy. The objective of this study was to evaluate the survival benefit of administering sapacitabine, an oral nucleoside analogue, in alternating cycles with decitabine, a low-intensity therapy, to elderly patients with newly diagnosed AML.
Methods: This randomized, open-label, phase 3 study (SEAMLESS) was conducted at 87 sites in 11 countries. Patients aged ≥70 years who were not candidates for or chose not to receive standard induction chemotherapy were randomized 1:1 to arm A (decitabine in alternating cycles with sapacitabine) received 1-hour intravenous infusions of decitabine 20 mg/m2 once daily for 5 consecutive days every 8 weeks (first cycle and subsequent odd cycles) and sapacitabine 300 mg twice daily on 3 consecutive days per week for 2 weeks every 8 weeks (second cycle and subsequent even cycles) or to control arm C who received 1-hour infusions of decitabine 20 mg/m2 once daily for 5 consecutive days every 4 weeks. Prior hypomethylating agent therapy for preexisting myelodysplastic syndromes or myeloproliferative neoplasms was an exclusion criterion. Randomization was stratified by antecedent myelodysplastic syndromes or myeloproliferative neoplasms, white blood cell count (<10 × 109 /L and ≥10 × 109 /L), and bone marrow blast percentage (≥50% vs <50%). The primary end point was overall survival (OS). Secondary end points were the rates of complete remission (CR), CR with incomplete platelet count recovery, partial remission, hematologic improvement, and stable disease along with the corresponding durations, transfusion requirements, number of hospitalized days, and 1-year survival. The trial is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01303796).
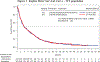
Results: Between October 2011 and December 2014, 482 patients were enrolled and randomized to receive decitabine administered in alternating cycles with sapacitabine (study arm, n = 241) or decitabine monotherapy (control arm, n = 241). The median OS was 5.9 months on the study arm versus 5.7 months on the control arm (P = .8902). The CR rate was 16.6% on the study arm and 10.8% on the control arm (P = .1468). In patients with white blood cell counts <10 × 109 /L (n = 321), the median OS was higher on the study arm versus the control arm (8.0 vs 5.8 months; P = .145), as was the CR rate (21.5% vs 8.6%; P = .0017).
Conclusions: The regimen of decitabine administered in alternating cycles with sapacitabine was active but did not significantly improve OS compared with decitabine monotherapy. Subgroup analyses suggest that patients with baseline white blood cell counts <10 × 109 /L might benefit from decitabine alternating with sapacitabine, with an improved CR rate and the convenience of an oral drug. These findings should be prospectively confirmed.
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia (AML); decitabine; hypomethylation; sapacitabine; therapy.
© 2021 American Cancer Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
Hagop M. Kantarjian reports research grants and honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Ascentage, BMS, Daiichi-Sankyo, Immunogen, Jazz, Novartis, Pfizer and Sanofi; honoraria from Actinium (Advisory Board), Adaptive Biotechnologies, Aptitude Health, BioAscend, Delta Fly, Janssen Global, Oxford Biomedical and Takeda. Stephen Strickland reports AbbVie, ArcherDx, Genentech, Incyte, Kura Oncology, Novartis, Pfizer, and Syros; Research Funding (paid t institution): Sunesis. Marc Buys reports being a shareholder of IDDI (International drug Development Institute, Belgium). Tapan M. Kadia reports consulting fees from AbbVie, Agios, Daiichi Sankyo, Genetech,Jazz, Liberum, Novartis, Phizer, Sanofi-Aventis; Grant Research Support from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Genetech, Jazz, Pfizer, Pulmotech, Cellenkos, Ascentage, Genfleet, Astellas, Astrazeneca; Speaker’s Bureau from Cure and honoraria from Genzyme. The other authors made no disclosures.
Figures
References
-
- Tallman MS, Gilliland DG, Rowe JM. Drug therapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2005; 106: 1154–1163. - PubMed
-
- Nieto M, Demolis P, Behanzin E, et al. The European Medicines Agency Review of Decitabine (Dacogen) for the Treatment of Adult Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Summary of the Scientific Assessment of the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. The Oncologist. 2016; 21: 692–700. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shallis RM, Wang R, Davidoff A, Ma X, Podoltsev NA, Zeidan AM. Epidemiology of acute myeloid leukemia: Recent progress and enduring challenges. Blood Rev. 2019; 36: 70–87. - PubMed
-
- National Cancer Institute. NCI Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program Cancer Statistics Review (CSR) 1975–2014. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2015/results_single/sect_13_table.14.pdf (accessed May 13, 2018)