IgG4-related hepatic inflammatory pseudotumour: could MRI suggest the correct diagnosis?
- PMID: 34426430
- PMCID: PMC8383849
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2021-244572
IgG4-related hepatic inflammatory pseudotumour: could MRI suggest the correct diagnosis?
Abstract
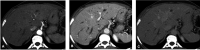
We report a case of a 62-year-old woman, HIV positive, with a 3-week history of jaundice and elevated cholestatic enzymes. Imaging studies displayed intrahepatic biliary dilatation and a central liver lesion. Pathology described lesions of active cholangitis, lymphoplasmacytic infiltration and fibrosis, suggesting a hepatic inflammatory pseudotumour (IPT) IgG4 related. IgG4-related lymphoplasmacytic form of IPT belongs to IgG4-related diseases. We discuss the importance to include IgG4-related hepatic IPT as part of the differential diagnosis of any liver lesion, highlighting potential imaging clues that may help in establishing the correct diagnosis.
Keywords: gastrointestinal system; liver disease; radiology (diagnostics).
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2021. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures




References
-
- Umiker WO, Iverson L. Postinflammatory tumors of the lung; report of four cases simulating xanthoma, fibroma, or plasma cell tumor. J Thorac Surg 1954;28:55–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
