Cavβ3 Regulates Ca2+ Signaling and Insulin Expression in Pancreatic β-Cells in a Cell-Autonomous Manner
- PMID: 34426509
- PMCID: PMC8564405
- DOI: 10.2337/db21-0078
Cavβ3 Regulates Ca2+ Signaling and Insulin Expression in Pancreatic β-Cells in a Cell-Autonomous Manner
Abstract
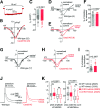
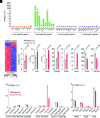
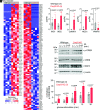
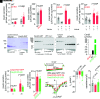
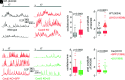
Voltage-gated Ca2+ (Cav) channels consist of a pore-forming Cavα1 subunit and auxiliary Cavα2-δ and Cavβ subunits. In fibroblasts, Cavβ3, independent of its role as a Cav subunit, reduces the sensitivity to low concentrations of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3). Similarly, Cavβ3 could affect cytosolic calcium concentration ([Ca2 +]) in pancreatic β-cells. In this study, we deleted the Cavβ3-encoding gene Cacnb3 in insulin-secreting rat β-(Ins-1) cells using CRISPR/Cas9. These cells were used as controls to investigate the role of Cavβ3 on Ca2+ signaling, glucose-induced insulin secretion (GIIS), Cav channel activity, and gene expression in wild-type cells in which Cavβ3 and the IP3 receptor were coimmunoprecipitated. Transcript and protein profiling revealed significantly increased levels of insulin transcription factor Mafa, CaMKIV, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type-1, and nitric oxide synthase-1 in Cavβ3-knockout cells. In the absence of Cavβ3, Cav currents were not altered. In contrast, CREB activity, the amount of MAFA protein and GIIS, the extent of IP3-dependent Ca2+ release and the frequency of Ca2+ oscillations were increased. These processes were decreased by the Cavβ3 protein in a concentration-dependent manner. Our study shows that Cavβ3 interacts with the IP3 receptor in isolated β-cells, controls IP3-dependent Ca2+-signaling independently of Cav channel functions, and thereby regulates insulin expression and its glucose-dependent release in a cell-autonomous manner.
© 2021 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures


References
-
- Ashcroft FM, Rorsman P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic beta-cell. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 1989;54:87–143 - PubMed
-
- Grapengiesser E, Gylfe E, Hellman B. Glucose-induced oscillations of cytoplasmic Ca2+ in the pancreatic beta-cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1988;151:1299–1304 - PubMed
-
- Henquin JC, Meissner HP. Significance of ionic fluxes and changes in membrane potential for stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic B-cells. Experientia 1984;40:1043–1052 - PubMed
-
- Kindmark H, Köhler M, Efendić S, Rorsman P, Larsson O, Berggren PO. Protein kinase C activity affects glucose-induced oscillations in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ in the pancreatic B-cell. FEBS Lett 1992;303:85–90 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

