Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with algae and the importance of capping agents in the process
- PMID: 34427807
- PMCID: PMC8385017
- DOI: 10.1186/s43141-021-00228-w
Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with algae and the importance of capping agents in the process
Abstract
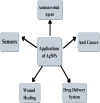
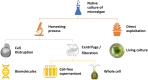
Background: Nanoparticle synthesis is a very interesting area of research currently due to the wide applications of nanoparticles. The nanoparticles have a diameter ranging between 1 and 100 nm and they are used in different fields like electronics, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, biotechnology, medicines, etc. Nanoparticles have gained the interest of researchers due to their large surface-to-volume ratio and their capability to interact effectively with other particles. Several different methods can be used for the production of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) including chemical, physical, and biological. Out of all the methods, the biological method is considered the cleanest and safest as no toxic chemicals are used in the process. The biological method includes the use of bacteria, fungi, algae, and plant extract for the synthesis. Algal synthesis of AgNPs is especially interesting because of the high capacity of the algae to take in metals and reduce metal ions. Algae is a widely distributed organism and its availability is abundant; an added advantage is their growth under laboratory conditions. These organisms can help in large-scale production at a low cost.
Short conclusion: This review article explains the different factors that should be considered for the effective synthesis of AgNPs using algae. Capping agents also affect the stability of nanoparticles. It also sheds light on the importance of capping agents in the synthesis of AgNPs. Alga-mediated synthesis of AgNPs along with the use of different capping agents can help in modulating the stability and size of the nanoparticles, thereby improving its cost-effectiveness and environment-friendly production.
Keywords: Algal synthesis; Capping agent; Green synthesis; Silver nanoparticles; Transmission electron microscope.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Kim SH, Lee HS, Ryu DS, Choi SJ, Lee DS. Antibacterial activity of silver-nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Korean J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011;39(1):77–85.
-
- Prabhu S, Poulose EK. Silver nanoparticles: mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int Nano Lett. 2012;2(1):32. doi: 10.1186/2228-5326-2-32. - DOI
-
- Gholami-Shabani M, Akbarzadeh A, Norouzian D, Amini A, Gholami-Shabani Z, Imani A, Chiani M, Riazi G, Shams-Ghahfarokhi M, Razzaghi-Abyaneh M. Antimicrobial activity and physical characterization of silver nanoparticles green synthesized using nitrate reductase from Fusarium oxysporum. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014;172(8):4084–4098. doi: 10.1007/s12010-014-0809-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
