Lack of pharmacokinetic interaction between the HIV-1 maturation inhibitor GSK3640254 and combination oral contraceptives in healthy women
- PMID: 34427938
- PMCID: PMC9291532
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.15051
Lack of pharmacokinetic interaction between the HIV-1 maturation inhibitor GSK3640254 and combination oral contraceptives in healthy women
Abstract
Aims: GSK3640254 is a next-generation maturation inhibitor likely to be coadministered with combined oral contraceptives in HIV-positive women.
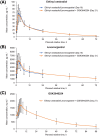
Methods: This phase I, open-label, 1-way study assessed pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions of GSK3640254 200 mg and ethinyl oestradiol 0.03 mg/levonorgestrel 0.15 mg once daily in healthy female participants who received ethinyl oestradiol/levonorgestrel for 10 days with a moderate-fat meal after which GSK3640254 was added from Days 11 to 21. Primary endpoints were area under the plasma concentration-time curve to the end of the dosing interval (AUC0-t ), maximum observed concentration (Cmax ) and plasma concentration at the end of the dosing interval (Cτ ) for ethinyl oestradiol and levonorgestrel. Serum follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone and progesterone concentrations were determined. Adverse events were monitored.
Results: Among 23 enrolled participants, 17 completed the study. Geometric least squares mean ratios (with vs. without GSK3640254) of AUC0-t , Cmax and Cτ were 0.974, 0.970 and 1.050 for ethinyl oestradiol and 1.069, 1.032 and 1.083 for levonorgestrel, respectively. Three participants had elevated progesterone levels, which occurred before GSK3640254 administration in 2 participants. No participants had elevated follicle-stimulating hormone or luteinizing hormone values. Fourteen participants (61%) reported adverse events. Four participants reported asymptomatic elevated transaminase levels meeting liver-stopping criteria; of these, 3 events occurred before GSK3640254 administration and led to study withdrawal.
Conclusion: Ethinyl oestradiol/levonorgestrel plus GSK3640254 coadministration did not affect steady-state pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of ethinyl oestradiol and levonorgestrel in healthy female participants. No major tolerability findings were reported. Elevated liver transaminase levels were probably due to ethinyl oestradiol/levonorgestrel.
Keywords: HIV infection; drug-drug interaction; ethinyl oestradiol; levonorgestrel; pharmacodynamics.
© 2021 ViiV Healthcare. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
T.P. and J.X. were employees of GlaxoSmithKline at the time of the study and may hold stock in the company. T.J.G., F.H. and L.B. are employees of and own stock in GlaxoSmithKline. S.R.J. is an employee of ViiV Healthcare. M.J., M.L. and S.M. are employees of ViiV Healthcare and own stock in GlaxoSmithKline. E.Z. and L.W. are employees of PPD. T.T.P. was an employee of PPD at the time of the study.
Figures
References
-
- Morales‐Ramirez J, Bogner JR, Molina J‐M, et al. Safety, efficacy, and dose response of the maturation inhibitor GSK3532795 (formerly known as BMS‐955176) plus tenofovir/emtricitabine once daily in treatment‐naive HIV‐1‐infected adults: week 24 primary analysis from a randomized phase IIb trial. PLoS One. 2018;13(10):e0205368. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smith PF, Ogundele A, Forrest A, et al. Phase I and II study of the safety, virologic effect, and pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of single‐dose 3‐o‐(3′,3′‐dimethylsuccinyl)betulinic acid (bevirimat) against human immunodeficiency virus infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007;51(10):3574‐3581. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

