Discovery of Cellular RhoA Functions by the Integrated Application of Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
- PMID: 34429388
- PMCID: PMC8724844
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2021.075
Discovery of Cellular RhoA Functions by the Integrated Application of Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
Abstract
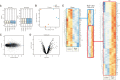
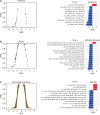
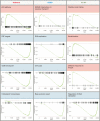
The small GTPase RhoA has been studied extensively for its role in actin dynamics. In this study, multiple bioinformatics tools were applied cooperatively to the microarray dataset GSE64714 to explore previously unidentified functions of RhoA. Comparative gene expression analysis revealed 545 differentially expressed genes in RhoA-null cells versus controls. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was conducted with three gene set collections: (1) the hallmark, (2) the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway, and (3) the Gene Ontology Biological Process. GSEA results showed that RhoA is related strongly to diverse pathways: cell cycle/growth, DNA repair, metabolism, keratinization, response to fungus, and vesicular transport. These functions were verified by heatmap analysis, KEGG pathway diagramming, and direct acyclic graphing. The use of multiple gene set collections restricted the leakage of information extracted. However, gene sets from individual collections are heterogenous in gene element composition, number, and the contextual meaning embraced in names. Indeed, there was a limit to deriving functions with high accuracy and reliability simply from gene set names. The comparison of multiple gene set collections showed that although the gene sets had similar names, the gene elements were extremely heterogeneous. Thus, the type of collection chosen and the analytical context influence the interpretation of GSEA results. Nonetheless, the analyses of multiple collections made it possible to derive robust and consistent function identifications. This study confirmed several well-described roles of RhoA and revealed less explored functions, suggesting future research directions.
Keywords: GSE64714; Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA); Gene ontology; Hallmark pathway; Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway; RhoA.
Figures









References
-
- Adnane J., Muro-Cacho C., Mathews L., Sebti S. M., Munoz-Antonia T. Suppression of rho B expression in invasive carcinoma from head and neck cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002;8:2225–2232. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner M., Ball C. A., Blake J. A., Botstein D., Butler H., Cherry J. M., Davis A. P., Dolinski K., Dwight S. S., Eppig J. T., Harris M. A., Hill D. P., Issel-Tarver L., Kasarskis A., Lewis S., Matese J. C., Richardson J. E., Ringwald M., Rubin G. M., Sherlock G. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000;25:25–29. doi: 10.1038/75556. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carlson M. mouse4302.db: Affymetrix Mouse Genome 430 2.0 Array annotation data (chip mouse4302) R package version 3.2.3. 2016.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

