Effect of Doxofylline on Reducing the Inflammatory Response in Mechanically Ventilated Rats with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 34429595
- PMCID: PMC8378927
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S315639
Effect of Doxofylline on Reducing the Inflammatory Response in Mechanically Ventilated Rats with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Retraction in
-
Effect of Doxofylline on Reducing the Inflammatory Response in Mechanically Ventilated Rats with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease [Retraction].Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023 May 26;18:1005-1006. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S422914. eCollection 2023. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023. PMID: 37260545 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effect of doxofylline on reducing the inflammatory response in mechanically ventilated rats with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
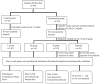
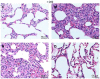
Methods: A total of 40 eight-week-old male Sprague Dawley rats were randomly divided into four groups of 10 rats each: a control group (group C), a model group (group M), a model + natural saline group (group N), and a doxofylline group (group D). Then mechanical ventilation, drug intervention, and the extraction of the experimental material were performed in each group. Pulmonary tissue samples were taken after 120 minutes of mechanical ventilation and the pulmonary histopathological changes and the wet/dry (W/D) weight ratio of the pulmonary tissue were identified. The levels of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and interleukin 10 (IL-10) were detected using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and the expression levels of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) and phosphorylated c-Jun N-terminal kinase (p-JNK) were detected using immunohistochemistry.
Results: Compared with group C, the pulmonary histopathology in groups M, N, and D showed typical changes associated with COPD. Furthermore, the W/D weight ratio and levels of TNF-α, JNK, and p-JNK in the pulmonary tissue increased in groups M, N, and D (P < 0.05), while the levels of IL-10 decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with group M, no statistically significant changes in the above indicators were detected in the pulmonary tissue of group N (P > 0.05). Compared with group N, the W/D weight ratio and levels of TNF-α, JNK, and p-JNK in the pulmonary tissue decreased in group D (P < 0.05), while the levels of IL-10 increased (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Doxofylline might attenuate pulmonary inflammatory responses in mechanically ventilated rats with COPD, and the JNK/stress-activated protein kinase signaling pathway is involved in doxofylline's inhibition of inflammatory responses in the pulmonary tissue of rats with COPD.
Keywords: IL-10; JNK; TNF-α; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; p-JNK.
© 2021 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of doxofylline on pulmonary inflammatory response and oxidative stress during mechanical ventilation in rats with COPD.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Feb 17;22(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-01859-6. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 35177065 Free PMC article.
-
Esketamine mitigates mechanical ventilation-induced lung injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease rats via inhibition of the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway and reduction of oxidative stress.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Sep 30;139:112725. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112725. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39059100
-
The Mechanism of Penehyclidine Hydrochloride and Its Effect on the Inflammatory Response of Lung Tissue in Rats with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease During Mechanical Ventilation.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021 Mar 31;16:877-885. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S295329. eCollection 2021. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021. Retraction in: Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023 May 26;18:1003-1004. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S422900. PMID: 33833508 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Electroacupuncture inhibits IL-17/IL-17R and post-receptor MAPK signaling pathways in a rat model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Acupunct Med. 2021 Dec;39(6):663-672. doi: 10.1177/0964528421996720. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Acupunct Med. 2021. PMID: 33715422
-
Impact of doxofylline in COPD: A pairwise meta-analysis.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Aug;51:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2018.04.010. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29705620 Review.
Cited by
-
Correction: Effect of doxofylline on pulmonary inflammatory response and oxidative stress during mechanical ventilation in rats with COPD.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 May 14;24(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03049-y. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 38745138 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The effects of camel milk in systemic inflammation and oxidative stress of cigarette smoke-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease model in rat.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Dec 13;11:1464432. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1464432. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39735585 Free PMC article.
-
Camel milk inhibits pulmonary oxidative stress and inflammation in a rat model of COPD induced by cigarette smoke exposure.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 16;10(20):e39416. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39416. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39497967 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of autophagy-related genes in the therapeutic effects of Xuanfei Pingchuan capsules on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease based on transcriptome sequencing analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 May 18;14:1123882. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1123882. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37274101 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

