Identification of Novel Ligands for Targeted Antifibrotic Therapy of Chronic Pancreatitis
- PMID: 34429596
- PMCID: PMC8374843
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S318331
Identification of Novel Ligands for Targeted Antifibrotic Therapy of Chronic Pancreatitis
Abstract
Purpose: Chronic pancreatitis (CP) is an inflammatory disorder of the pancreas that leads to impaired pancreatic function. The limited therapeutic options and the lack of molecular targeting ligands or non-serum-based biomarkers hinder the development of target-specific drugs. Thus, there is a need for an unbiased, comprehensive discovery and evaluation of pancreatitis-specific ligands.
Methods: This study utilized a computational-guided in vivo phage display approach to select peptide ligands selective for cellular components in the caerulein-induced mouse model of CP. The identified peptides were conjugated to pegylated DOPC liposomes via the reverse-phase evaporation method, and the in vivo specificity and pharmacokinetics were determined. As proof of concept, CP-targeted liposomes were used to deliver an antifibrotic small molecular drug, apigenin. Antifibrotic effects determined by pancreatic histology, fibronectin expression, and collagen deposition were evaluated.
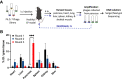
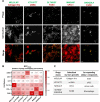
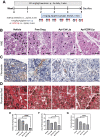
Results: We have identified five peptides specific for chronic pancreatitis and demonstrated selectivity to activated pancreatic stellate cells, acinar cells, macrophages, and extracellular matrix, respectively. MDLSLKP-conjugated liposomes demonstrated an increased particle accumulation by 1.3-fold in the inflamed pancreas compared to the control liposomes. We also observed that targeted delivery of apigenin resulted in improved acini preservation, a 37.2% and 33.1% respective reduction in collagen and fibronectin expression compared to mice receiving the free drug, and reduced oxidative stress in the liver.
Conclusion: In summary, we have developed a systematic approach to profile peptide ligands selective for cellular components of complex disease models and demonstrated the biomedical applications of the identified peptides to improve tissue remodeling in the inflamed pancreas.
Keywords: drug delivery; next-generation sequencing; peptide ligands; phage display; targeted liposomes.
© 2021 Hung et al.
Conflict of interest statement
KAK is the CEO and Founder of ZielBio, Inc. ZielBio played no role in funding this work. KAK and JH report a patent HIGH-THROUGHPUT ANALYTIC SELECTIONS OF NOVEL TARGETING LIGANDS FOR CHRONIC PANCREATITIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF TARGET-SPECIFIC LIPOSOMES FOR ANTIFIBROTIC THERAPY pending to United States Patent and Trademark Office. The application was filed on 2/5/2021. ALK is a subcontract of an NIH grant to SoundPipe Therapeutics, a company in the area of microbubble-assisted drug delivery. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

