Acute anti-Ma2 paraneoplastic encephalitis associated to pembrolizumab: a case report and review of literature
- PMID: 34430366
- PMCID: PMC8350103
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-21-222
Acute anti-Ma2 paraneoplastic encephalitis associated to pembrolizumab: a case report and review of literature
Abstract
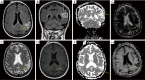
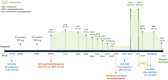
Anti-Ma2 encephalitis is a rare neurological disorder with a predominant involvement of brainstem, limbic and diencephalic structures. Although an unspecific encephalopathy is the usual form of presentation, acute-onset neurologic symptoms and other atypical manifestations have been described and account for the challenging diagnosis of this entity. Despite being usually detected as a paraneoplastic syndrome in patients with early-stage tumors or without a previous history of malignancy, a growing concern has arisen from several cases reported in metastatic patients under treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors. We report what to our knowledge is the first known case of anti-Ma2 encephalitis associated to pembrolizumab and presenting as an acute-onset focal neurological syndrome, consisting on acute global aphasia, right upper limb paresia, hypoacusia, sleep disorder, decreased conscious level and a motor focal status that was refractory to anticonvulsant therapy. A brain MRI scan showed a focal alteration of the cortical-subcortical signal on the left parietal lobe. CSF study found a significant hyperproteinorrhachia and electroencephalography showed lateralized periodic discharges (LPDs), suggestive of a diffuse encephalopathy. A positive result for anti-Ma2 antibodies was obtained both in blood and CSF samples through indirect immune-fluorescence (IFI) and later confirmed by western-blot technique. Our patient obtained a mild response to steroid therapy and a significant improvement after the administration of intravenous immunoglobulins. The hypothesis that checkpoint inhibitors may trigger the expression of previously subclinical paraneoplastic events, through the strengthening of cytotoxic T cells-mediated immune response, is supported by our finding of preexisting anti-Ma2 antibodies in preserved blood samples obtained before the initiation of pembrolizumab in our patient. Further research is needed to reveal if the detection of onconeural antibodies prior to a treatment with checkpoint inhibitors may be used as a predictive biomarker of neurologic immune-related high-grade toxicity.
Keywords: Anti-Ma2; case report; checkpoint inhibitors; encephalitis; paraneoplastic.
2021 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tlcr-21-222). PG declares personal financial interests as advisor for Abbvie, AstraZeneca, Blueprint Medicines, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol, Gilead, Guardant Health, Janssen, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Rovi, Sysmex and Takeda. AS reports personal fees from Merck, Bristol and Roche. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
