Indian Expert Opinion on Cancer Care during COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 34430513
- PMCID: PMC8380145
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0041-1727560
Indian Expert Opinion on Cancer Care during COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
Coronavirus pandemic has increased human disease burden, as well as economic distress globally. Being in an immunocompromised state, patients with cancer comprise an important at-risk population for novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection. It is necessary to modify individualized clinical management for every cancer patient in the context of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. Simultaneously, additional safety precautions for the cancer care providers are mandatory. This review will provide general recommendations in the Indian context optimizing the same.
Keywords: India; oncology management; patient safety; recommendations.
MedIntel Services Pvt Ltd. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial-License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



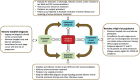
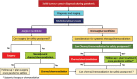
References
-
- WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard. Available at: https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed June 12, 2020
-
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Government of India. COVID-19 Statewise status. Available at: https://www.mohfw.gov.in/. Accessed June 12, 2020
-
- Mehta P, Parikh P, Aggarwal S et al.Has India met this enemy before? From an eternal optimist’s perspective: SARS-CoV-2. Indian J Med Sci. 2020;72(01):8–12.
-
- Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Available at: who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/who-china-joint-mission-on-covi.... Accessed April 29, 2020
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

