Convenience and satisfaction in direct oral anticoagulant-treated patients with atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 34430791
- PMCID: PMC8371341
- DOI: 10.1002/rth2.12577
Convenience and satisfaction in direct oral anticoagulant-treated patients with atrial fibrillation
Abstract
Background: Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are the preferred anticoagulants for thromboprophylaxis in atrial fibrillation. We aimed to identify determinants of quality of life related to DOAC treatment to optimize DOAC treatment convenience and satisfaction.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study in DOAC users. DOAC treatment-related convenience and satisfaction were measured by Perception of Anticoagulant Treatment Questionnaire. Higher scores are more favorable (range, 0-100). Patient-reported outcome measures and drug- and organization-related factors were collected. Multiple regression analyses were used to evaluate the association between these factors (ie, exposure variables) and DOAC treatment-related convenience and treatment satisfaction (ie, outcome variables).
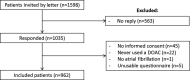
Results: Of 1598 patients invited, 1035 responded, and 962 were included. The median convenience score was 98.1 (94.2-100.0), mean satisfaction score 66.5± 14.9. Twenty-four percent felt not well informed at the start of DOAC; 6.9% did not know who to turn to with questions. Multiple regression analyses showed that lacking sense of security, the predefined composite of receiving insufficient information at start of DOAC and/or not knowing who to turn to with questions was associated with lower convenience (regression coefficient, -1.29; 95% confidence interval [CI], -2.16 to -0.41). Bleeding, gastrointestinal complaints, and lower medication adherence were also associated with lower convenience. Missing sense of security (regression coefficient -6.59; 95% CI, -8.94 to -4.24) and bleeding without consultation were associated with lower treatment satisfaction.
Conclusions: Accessible interventions to improve DOAC care could be providing more instruction at treatment initiation and ensuring that patients know who to contact in case of problems.
Keywords: anticoagulants; atrial fibrillation; medication adherence; patient reported outcome measures; quality of life.
© 2021 The Authors. Research and Practice in Thrombosis and Haemostasis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH).
Figures
References
-
- Lloyd‐Jones DM, Wang TJ, Leip EP, et al. Lifetime risk for development of atrial fibrillation: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2004;110(9):1042‐1046. - PubMed
-
- Wolf PA, Abbott RD, Kannel WB. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: The Framingham Study. Stroke. 1991;22(8):983‐988. - PubMed
-
- Camm AJ, Lip GYH, De Caterina R, et al. 2012 focused update of the ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(21):2719‐2747. - PubMed
-
- Stichting Farmacaeutische Kengetallen . I. ISBN/EAN 978‐90‐830805‐0‐5. 2020. August.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources