Vitamin D supplementation for chronic liver diseases in adults
- PMID: 34431511
- PMCID: PMC8407054
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011564.pub3
Vitamin D supplementation for chronic liver diseases in adults
Abstract
Background: Vitamin D deficiency is often reported in people with chronic liver diseases. Improving vitamin D status could therefore be beneficial for people with chronic liver diseases.
Objectives: To assess the beneficial and harmful effects of vitamin D supplementation in adults with chronic liver diseases.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Hepato-Biliary Group Controlled Trials Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE Ovid, Embase Ovid, LILACS, Science Citation Index Expanded, and Conference Proceedings Citation Index-Science. We also searched ClinicalTrials.gov and the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform. We scanned bibliographies of relevant publications and enquired experts and pharmaceutical companies as to additional trials. All searches were up to November 2020.
Selection criteria: Randomised clinical trials that compared vitamin D at any dose, duration, and route of administration versus placebo or no intervention in adults with chronic liver diseases. Vitamin D could have been administered as supplemental vitamin D (vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) or vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol)), or an active form of vitamin D (1α-hydroxyvitamin D (alfacalcidol), 25-hydroxyvitamin D (calcidiol), or 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (calcitriol)).
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures expected by Cochrane. We used GRADE to assess the certainty of evidence.
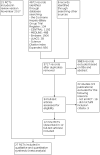
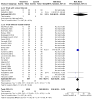
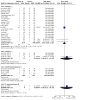
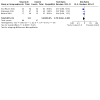
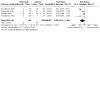
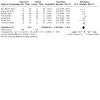
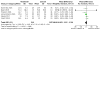
Main results: We included 27 randomised clinical trials with 1979 adult participants. This review update added 12 trials with 945 participants. We assessed all trials as at high risk of bias. All trials had a parallel-group design. Eleven trials were conducted in high-income countries and 16 trials in middle-income countries. Ten trials included participants with chronic hepatitis C, five trials participants with liver cirrhosis, 11 trials participants with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and one trial liver transplant recipients. All of the included trials reported the baseline vitamin D status of participants. Participants in nine trials had baseline serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels at or above vitamin D adequacy (20 ng/mL), whilst participants in the remaining 18 trials were vitamin D insufficient (less than 20 ng/mL). Twenty-four trials administered vitamin D orally, two trials intramuscularly, and one trial intramuscularly and orally. In all 27 trials, the mean duration of vitamin D supplementation was 6 months, and the mean follow-up of participants from randomisation was 7 months. Twenty trials (1592 participants; 44% women; mean age 48 years) tested vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol); three trials (156 participants; 28% women; mean age 54 years) tested vitamin D2; four trials (291 participants; 60% women; mean age 52 years) tested 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D; and one trial (18 participants; 0% women; mean age 52 years) tested 25-hydroxyvitamin D. One trial did not report the form of vitamin D. Twelve trials used a placebo, whilst the other 15 trials used no intervention in the control group. Fourteen trials appeared to be free of vested interest. Eleven trials did not provide any information on clinical trial support or sponsorship. Two trials were funded by industry. We are very uncertain regarding the effect of vitamin D versus placebo or no intervention on all-cause mortality (risk ratio (RR) 0.86, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.51 to 1.45; 27 trials; 1979 participants). The mean follow-up was 7 months (range 1 to 18 months). We are very uncertain regarding the effect of vitamin D versus placebo or no intervention on liver-related mortality (RR 1.62, 95% CI 0.08 to 34.66; 1 trial; 18 participants) (follow-up: 12 months); serious adverse events such as hypercalcaemia (RR 5.00, 95% CI 0.25 to 100.8; 1 trial; 76 participants); myocardial infarction (RR 0.75, 95% CI 0.08 to 6.81; 2 trials; 86 participants); thyroiditis (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.01 to 7.91; 1 trial; 68 participants); circular haemorrhoidal prolapse (RR 3.00, 95% CI 0.14 to 65.9; 1 trial; 20 participants); bronchopneumonia (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.02 to 7.32; 1 trial 20 participants); and non-serious adverse events. The certainty of evidence for all outcomes is very low. We found no data on liver-related morbidity such as gastrointestinal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy, hepatorenal syndrome, ascites, or liver cancer. There were also no data on health-related quality of life. The evidence is also very uncertain regarding the effect of vitamin D versus placebo or no intervention on rapid, early, and sustained virological response in people with chronic hepatitis C.
Authors' conclusions: Given the high risk of bias and insufficient power of the included trials and the very low certainty of the available evidence, vitamin D supplementation versus placebo or no intervention may increase or reduce all-cause mortality, liver-related mortality, serious adverse events, or non-serious adverse events in adults with chronic liver diseases. There is a lack of data on liver-related morbidity and health-related quality of life. Further evidence on clinically important outcomes analysed in this review is needed.
Copyright © 2021 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
MB: none known. DN is the Managing Editor of the Cochrane Hepato‐Biliary Group. However, the peer review process was dealt with through staff within the Cochrane Central Editorial Service Team. GB: none known. CG: none known.
Figures






























Update of
-
Vitamin D supplementation for chronic liver diseases in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 3;11(11):CD011564. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011564.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Aug 25;8:CD011564. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011564.pub3. PMID: 29099543 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Abu‐Mouch 2011 {published data only}
Atsukawa 2016 {published data only}
-
- Atsukawa M, Tsubota A, Shimada N, Yoshizawa K, Abe H, Asano T, et al. Effect of native vitamin D3 supplementation on refractory chronic hepatitis C patients in simeprevir with pegylated interferon/ribavirin. Hepatology Research 2016;46(5):450-8. - PubMed
Barchetta 2016 {published data only}
Behera 2018 {published data only}
Boonyagard 2016 {published data only}
-
- Boonyagard S, Techatuvanan K. Impact of vitamin D replacement on liver enzymes in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2016;64(S1):542.
Dabbaghmanesh 2018 {published data only}
-
- Dabbaghmanesh MH, Danafar F, Eshraghian A, Omrani GR. Vitamin D supplementation for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized double blind placebo controlled trial. Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome 2018;12(4):513-7. - PubMed
Esmat 2015 {published data only}
-
- Esmat G, El Raziky M, Elsharkawy A, Sabry D, Hassany M, Ahmed A, et al. Impact of vitamin D supplementation on sustained virological response in chronic hepatitis C genotype 4 patients treated by pegylated interferon/ribavirin. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research 2015;35(1):49-54. - PubMed
Foroughi 2016 {published data only}
Geier 2018 {published data only}
-
- Geier A, Eichinger M, Stirnimann G, Semela D, Tay F, Seifert B, et al. Treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis patients with vitamin D: a double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled pilot study. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2018;53(9):1114-20. - PubMed
Hosseini 2018 {published data only}
-
- Hosseini SM, Aliashrafi S, Ebrahimi-Mameghani M. The effect of a single intramuscular injection of cholecalciferol on the serum levels of vitamin D, adiponectin, insulin resistance, and liver function in women with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal 2018;20(10):1-12.
Hussain 2019 {published data only}
-
- Hussain M, Iqbal J, Malik SA, Waheed A, Shabnum S, Akhtar L, et al. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on various parameters in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2019;32(3 Special):1343-8. - PubMed
Jeong 2019 {published data only}
Jha 2017 {published data only}
Komolmit 2017a {published data only}
-
- Komolmit P, Charoensuk K, Thanapirom K, Suksawatamnuay S, Thaimai P, Chirathaworn C, et al. Correction of vitamin D deficiency facilitated suppression of IP-10 and DPP IV levels in patients with chronic hepatitis C: a randomised double-blinded, placebo-control trial. PLOS ONE 2017;12(4):e0174608. - PMC - PubMed
Komolmit 2017b {published data only}
-
- Komolmit P, Kimtrakool S, Suksawatamnuay S, Thanapirom K, Chattrasophon K, Thaimai P, et al. Vitamin D supplementation improves serum markers associated with hepatic fibrogenesis in chronic hepatitis C patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Scientific Reports 2017;7(1):8905. - PMC - PubMed
Lorvand Amiri 2016 {published data only}
-
- Lorvand Amiri H, Agah S, Mousavi SN, Hosseini AF, Shidfar F. Regression of non-alcoholic fatty liver by vitamin D supplement: a double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial. Archives of Iranian Medicine 2016;19(9):631-8. - PubMed
-
- Lorvand Amiri H, Agah S, Tolouei Azar J, Hosseini S, Shidfar F, Mousavi SN. Effect of daily calcitriol supplementation with and without calcium on disease regression in non-alcoholic fatty liver patients following an energy-restricted diet: randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Clinical Nutrition 2016;16:31260-2. - PubMed
-
- Shidfar F, Mousavi SN, Lorvand Amiri H, Agah S, Hoseini S, Hajimiresmail SJ. Reduction of some atherogenic indices in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver by vitamin D and calcium co-supplementation: a double blind randomized controlled clinical trial. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2019;18(1):496-505. - PMC - PubMed
Mobarhan 1984 {published data only}
-
- Mobarhan SA, Russell RM, Recker RR, Posner DB, Iber FL, Miller P. Metabolic bone disease in alcoholic cirrhosis: a comparison of the effect of vitamin D2, 25-hydroxyvitamin D, or supportive treatment. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 1984;4(2):266-73. - PubMed
Nimer 2012 {published data only}
Pilz 2016 {published data only}
Sakpal 2017 {published data only}
Sharifi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Sharifi N, Amani R, Hajiani E, Cheraghian B. Does vitamin D improve liver enzymes, oxidative stress, and inflammatory biomarkers in adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? A randomized clinical trial. Endocrine 2014;47(1):70-80. - PubMed
Shiomi 1999a {published data only}
-
- Shiomi S, Masaki K, Habu D, Takeda T, Nishiguchi S, Kuroki T, et al. Calcitriol for bone disease in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 1999;14(6):547-52. - PubMed
Shiomi 1999b {published data only}
-
- Shiomi S, Masaki K, Habu D, Takeda T, Nishiguchi S, Kuroki T, et al. Calcitriol for bone loss in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Journal of Gastroenterology 1999;34(2):241-5. - PubMed
Taghvaei 2018 {published data only}
-
- Taghvaei T, Akha O, Mouodi M, Fakheri HT, Kashi Z, Maleki I, et al. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Acta Medica Mediterranea 2018;34:415–22.
Vosoghinia 2016 {published data only}
-
- Vosoghinia H, Esmaeilzadeh A, Ganji A, Hosseini SM, Jamehdar SA, Salehi M, et al. Vitamin D in standard HCV regimen (PEG-Interferon plus Ribavirin), its effect on the early virologic response rate: a clinical trial. Razavi International Journal of Medicine 2016;4(2):e36632.
Xing 2013 {published data only}
-
- Xing T, Qiu G, Zhong L, Ling L, Huang L, Peng Z. Calcitriol reduces the occurrence of acute cellular rejection of liver transplants: a prospective controlled study. Pharmazie 2013;68(10):821-6. - PubMed
Yokoyama 2014 {published data only}
-
- Yokoyama S, Takahashi S, Kawakami Y, Hayes CN, Kohno H, Kohno H, et al. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on pegylated interferon/ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C genotype 1b: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2014;21(5):348-56. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Atsukawa 2013 {published data only}
Benetti 2008 {published data only}
-
- Benetti A, Crosignani A, Varenna M, Giussani CS, Allocca M, Zuin M, et al. Primary biliary cirrhosis is not an additional risk factor for bone loss in women receiving regular calcium and vitamin D supplementation: a controlled longitudinal study. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 2008;42(3):306-11. - PubMed
Bitetto 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bitetto D, Fabris C, Fornasiere E, Pipan C, Fumolo E, Cussigh A, et al. Vitamin D supplementation improves response to antiviral treatment for recurrent hepatitis C. Transplant International 2011;24(1):43-50. - PubMed
Chen 2015 {published data only}
Dasarathy 2017 {published data only}
Fernández Fernández 2016 {published data only}
-
- Fernández Fernández N, Linares Torres P, Joáo Matias D, Jorquera Plaza F, Olcoz Goñi JL. Vitamin D deficiency in chronic liver disease, clinical-epidemiological analysis and report after vitamin D supplementation [Déficit de vitamina D en la enfermedad hepática crónica, análisis clínico epidemiológico y tras aporte vitamínico]. Gastroenterologia y Hepatologia 2016;39(5):305-10. - PubMed
Floreani 2007 {published data only}
-
- Floreani A, Carderi I, Ferrara F, Rizzotto ER, Luisetto G, Camozzi V, et al. A 4-year treatment with clodronate plus calcium and vitamin D supplements does not improve bone mass in primary biliary cirrhosis. Digestive and Liver Disease 2007;39(6):544-8. - PubMed
Hasanain 2018 {published data only}
-
- Hasanain AF, Zayed AA, Mahdy RE, Nafee AM. Cholecalciferol for prophylaxis against antituberculosis therapy-induced liver disorders among naïve patients with pulmonary tuberculosis: a randomized, comparative study. International Journal of Mycobacteriology 2017;6:149-55. - PubMed
Kitson 2016 {published data only}
-
- Kitson MT, Pham A, Gordon A, Kemp W, Roberts SK. High-dose vitamin D supplementation and liver histology in NASH. Gut 2016;65(4):717-8. - PubMed
Kondo 2013 {published data only}
Ladero 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ladero JM, Torrejón MJ, Sánchez-Pobre P, Suárez A, Cuenca F, De la Orden V, et al. Vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D therapy in chronic hepatitis C. Annals of Hepatology 2013;12(2):199-204. - PubMed
Long 1978 {published data only}
Malham 2012 {published data only}
-
- Malham M, Jørgensen PS, Lauridsen AL, Ott P, Glerup H, Dahlerup JF. The effect of a single oral megadose of vitamin D provided as either ergocalciferol (D 2) or cholecalciferol (D 3) in alcoholic liver cirrhosis. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2012;24(2):172-8. - PubMed
Naderpoor 2018 {published data only}
-
- Naderpoor N, Mousa A, De Courten M, Scragg R, De Courten B. The relationship between 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and liver enzymes in overweight or obese adults: cross-sectional and interventional outcomes. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2018;177:193-9. - PubMed
Omori‐Mizuno 2015 {published data only}
-
- Omori-Mizuno Y, Nakayama N, Inao M, Funyu J, Asabe S, Tomita K, et al. Randomized study comparing vitamin D3 and 1α-hydroxyvitamin D3 in combination with pegylated interferon/ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2015;30(9):1384-90. - PubMed
Papapostoli 2016 {published data only}
-
- Papapostoli I, Lammert F, Stokes CS. Effect of short-term vitamin D correction on hepatic steatosis as quantified by controlled attenuation parameter (CAP). Journal of Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases 2016;25(2):175-81. - PubMed
Park 2017 {published data only}
Rode 2010 {published data only}
-
- Rode A, Fourlanos S, Nicoll A. Oral vitamin D replacement is effective in chronic liver disease [Fréquence du déficit en vitamine D et effet de la supplémentation orale au cours des maladies chroniques du foie]. Gastroentérologie Clinique et Biologique 2010;34(11):618-20. - PubMed
Stokes 2016 {published data only}
-
- Stokes CS, Grünhage F, Baus C, Volmer DA, Wagenpfeil S, Riemenschneider M, et al. Vitamin D supplementation reduces depressive symptoms in patients with chronic liver disease. Clinical Nutrition (Edinburgh, Scotland) 2016;35(4):950-7. - PubMed
Tavakoli 2019 {published data only}
-
- Tavakoli H, Rostami H, Avan A, Bagherniya M, Ferns GA, Khayyatzadeh SS. High dose vitamin D supplementation is associated with an improvement in serum markers of liver function. Biofactors 2019;45(3):335-42. - PubMed
Terrier 2015 {published data only}
Zhou 2019 {published data only}
-
- Zhou Q, Li L, Chen Y, Zhang J, Zhong L, Peng Z, et al. Vitamin D supplementation could reduce the risk of acute cellular rejection and infection in vitamin D deficient liver allograft recipients. International Immunopharmacology 2019;75:105811. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
IRCT2016020326342N1 {published data only}
-
- IRCT2016020326342N1. Effectiveness of vitamin D supplementation on severity of cirrhosis based on CHILD and MELD scores in patients with decompensate cirrhosis. en.irct.ir/trial/21847 (first received 28 February 2016).
NCT02779465 {published data only}
-
- NCT02779465. Oral vitamin D treatment for the prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma (VDHCC). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02779465 (first received 20 May 2016).
Additional references
Arteh 2010
-
- Arteh J, Narra S, Nair S. Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in chronic liver disease. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 2010;55(9):2624-8. - PubMed
Atef 2018
-
- Atef SH. Vitamin D assays in clinical laboratory: past, present and future challenges. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2018;175:136-7. - PubMed
Autier 2014
-
- Autier P, Boniol M, Mullie P. Vitamin D status and ill health: a systematic review. Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2014;2(1):76-89. - PubMed
Autier 2016
-
- Autier P. Vitamin D status as a synthetic biomarker of health status. Endocrine 2016;51(2):201-2. - PubMed
Balshem 2011
-
- Balshem H, Helfand M, Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):401-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Barbarawi 2019
Begg 1994
-
- Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994;50(4):1088-101. - PubMed
Bischoff‐Ferrari 2009
-
- Bischoff-Ferrari H. Vitamin D: what is an adequate vitamin D level and how much supplementation is necessary. Best Practice & Research. Clinical Rheumatology 2009;23(6):789-95. - PubMed
Bischoff‐Ferrari 2020
-
- Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Vellas B, Rizzoli R, Kressig RW, Da Silva JAP, Blauth M, et al. Effect of vitamin D supplementation, omega-3 fatty acid supplementation, or a strength-training exercise program on clinical outcomes in older adults: the DO-HEALTH randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2020;324(18):1855-68. - PMC - PubMed
Bitetto 2011
-
- Bitetto D, Fabris C, Falleti E, Toniutto P. Vitamin D deficiency and HCV chronic infection: what comes first. Journal of Hepatology 2011;55(4):944-5. - PubMed
Bitetto 2012
-
- Bitetto D, Fabris C, Fornasiere E, Pipan C, Fumolo E, Cussigh A, et al. Vitamin D supplementation improves response to antiviral treatment for recurrent hepatitis C. Transplant International 2012;24(1):43-50. - PubMed
Bjelakovic 2014a
Bjelakovic 2014b
Boesen 2021
-
- Boesen K. Methodological Limitations of Psychiatric Drug Trials with a Particular Focus on Extended-Release Methylphenidate (Metodebegraensninger i Psykiatriske Laegemiddelforsøg Med et Saerligt Fokus på Methylphenidat Depotpraeparater) [PhD thesis]. University of Copenhagen, 2020.
Bolland 2006
-
- Bolland MJ, Grey AB, Ames RW, Mason BH, Horne AM, Gamble GD, et al. Determinants of vitamin D status in older men living in a subtropical climate. Osteoporosis International 2006;17(12):1742-8. - PubMed
Bolland 2014
-
- Bolland MJ, Grey A, Gamble GD, Reid IR. The effect of vitamin D supplementation on skeletal, vascular, or cancer outcomes: a trial sequential meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2014;2(4):307-20. - PubMed
Bolland 2018
-
- Bolland MJ, Grey A, Avenell A. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on musculoskeletal health: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis. Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2018;6(11):847-58. - PubMed
Borenstein 2009
-
- Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins T, Rothstein HR. Introduction to Meta-Analysis. Chichester (UK): John Wiley & Sons, 2009.
Brok 2008
-
- Brok J, Thorlund K, Gluud C, Wetterslev J. Trial sequential analysis reveals insufficient information size and potentially false positive results in many meta-analyses. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61(8):763-9. - PubMed
Brok 2009
-
- Brok J, Thorlund K, Wetterslev J, Gluud C. Apparently conclusive meta-analyses may be inconclusive - trial sequential analysis adjustment of random error risk due to repetitive testing of accumulating data in apparently conclusive neonatal meta-analyses. International Journal of Epidemiology 2009;38(1):287-98. - PubMed
Cacopardo 2012
-
- Cacopardo B, Camma C, Petta S, Pinzone MR, Cappellani A, Zanghi A, et al. Diagnostic and therapeutical role of vitamin D in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Frontiers in Bioscience (Elite Edition) 2012;4:1276-86. - PubMed
Castellini 2018
Chan 2004
-
- Chan AW, Hróbjartsson A, Haahr MT, Gøtzsche PC, Altman DG. Empirical evidence for selective reporting of outcomes in randomized trials: comparison of protocols to published articles. JAMA 2004;291(20):2457-65. - PubMed
Chen 2014
-
- Chen EQ, Shi Y, Tang H. New insight of vitamin D in chronic liver diseases. Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International 2014;13(6):580-5. - PubMed
Chiang 2011
-
- Chiang KC, Yeh CN, Chen MF, Chen TC. Hepatocellular carcinoma and vitamin D: a review. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2011;26(11):1597-603. - PubMed
Cholongitas 2012
-
- Cholongitas E, Theocharidou E, Goulis J, Tsochatzis E, Akriviadis E, Burroughs K. Review article: the extra-skeletal effects of vitamin D in chronic hepatitis C infection. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2012;35(6):634-46. - PubMed
Cohen 1960
-
- Cohen J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educational and Psychological Measurement 1960;20:37-46.
Corey 2012
Davis 2007
-
- Davis CD, Dwyer JT. The "sunshine vitamin": benefits beyond bone? Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2007;99(21):1563-5. - PubMed
Dawson‐Hughes 2005
-
- Dawson-Hughes B, Heaney RP, Holick MF, Lips P, Meunier PJ, Vieth R. Estimates of optimal vitamin D status. Osteoporosis International 2005;16(7):713-6. - PubMed
Dawson‐Hughes 2010
-
- Dawson-Hughes B, Mithal A, Bonjour JP, Boonen S, Burckhardt P, Fuleihan GE, et al. IOF position statement: vitamin D recommendations for older adults. Osteoporosis International 2010;21(7):1151-4. - PubMed
Deeks 2021
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG, editor(s). Chapter 10: Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In: Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.2 (updated February 2021). Cochrane, 2021. Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook.
DeMets 1987
-
- DeMets DL. Methods for combining randomized clinical trials: strengths and limitations. Statistics in Medicine 1987;6(3):341-50. - PubMed
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7(3):177-88. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Elangovan 2017
-
- Elangovan H, Chahal S, Gunton JE. Vitamin D in liver disease: current evidence and potential directions. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 2017;1863(4):907-16. - PubMed
Eliades 2013
-
- Eliades M, Spyrou E, Agrawal N, Lazo M, Brancati FL, Potter JJ, et al. Meta-analysis: vitamin D and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2013;38(3):246-54. - PubMed
Eliades 2015
Farnik 2013
-
- Farnik H, Bojunga J, Berger A, Allwinn R, Waidmann O, Kronenberger B, et al. Low vitamin D serum concentration is associated with high levels of hepatitis B virus replication in chronically infected patients. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2013;58(4):1270-6. - PubMed
Finkelmeier 2014
-
- Finkelmeier F, Kronenberger B, Köberle V, Bojunga J, Zeuzem S, Trojan J, et al. Severe 25-hydroxyvitamin D deficiency identifies a poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma - a prospective cohort study. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2014;39(10):1204-12. - PubMed
Finkelmeier 2015
Fortmann 2013
-
- Fortmann SP, Burda BU, Senger CA, Lin JS, Whitlock EP. Vitamin and mineral supplements in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer: an updated systematic evidence review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Annals of Internal Medicine 2013;159(12):824-34. - PubMed
Furukawa 2007
-
- Furukawa TA, Watanabe N, Omori IM, Montori VM, Guyatt GH. Association between unreported outcomes and effect size estimates in Cochrane meta-analyses. JAMA 2007;297(5):468-70. - PubMed
Garattini 2016
-
- Garattini S, Jakobsen JC, Wetterslev J, Bertelé V, Banzi R, Rath A, et al. Evidence-based clinical practice: overview of threats to the validity of evidence and how to minimise them. European Journal of Internal Medicine 2016;32:13-21. - PubMed
Gartlehner 2019
-
- Gartlehner G, Nussbaumer-Streit B, Wagner G, Patel S, Swinson-Evans T, Dobrescu A, et al. Increased risks for random errors are common in outcomes graded as high certainty of evidence. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2019;106:50-9. - PubMed
Geier 2011
-
- Geier A. Shedding new light on vitamin D and fatty liver disease. Journal of Hepatology 2011;55(2):273-5. - PubMed
Gluud 2006
-
- Gluud C. The culture of designing hepato-biliary randomised trials. Journal of Hepatology 2006;44(3):607-15. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gluud 2007
-
- Gluud C, Brok J, Gong Y, Koretz RL. Hepatology may have problems with putative surrogate outcome measures. Journal of Hepatology 2007;46(4):734-42. - PubMed
Gluud 2008
-
- Gluud C, Hilden J. Povl Heiberg's 1897 methodological study on the statistical method as an aid in therapeutic trials, 2008. www.jameslindlibrary.org/articles/povl-heibergs-1897-methodological-stud... (accessed 17 July 2017). - PubMed
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime) GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 4 November 2020. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015. Available at gradepro.org.
Grey 2010
-
- Grey A, Bolland M. Vitamin D: a place in the sun. Archives of Internal Medicine 2010;170(13):1099-100. - PubMed
Guallar 2010
-
- Guallar E, Miller ER 3rd, Ordovas JM, Stranges S. Vitamin D supplementation in the age of lost innocence. Annals of Internal Medicine 2010;152(5):327-9. - PubMed
Guañabens 2010
-
- Guañabens N, Parés A. Liver and bone. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 2010;503(1):84-94. - PubMed
Guo 2020
-
- Guo XF, Wang C, Yang T, Li S, Li KL, Li D. Vitamin D and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food and Function 2020;11(9):7389-99. - PubMed
Gutierrez 2011
Guyatt 2011a
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction - GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):383-94. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011b
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Atkins D, Brozek J, Vist G, et al. GRADE guidelines: 2. Framing the question and deciding on important outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):395-400. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011c
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist G, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso-Coello P, et al. GRADE guidelines: 4. Rating the quality of evidence - study limitations (risk of bias). Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):407-15. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011d
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Montori V, Vist G, Kunz R, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 5. Rating the quality of evidence - publication bias. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1277-82. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011e
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso-Coello P, Rind D, et al. GRADE guidelines: 6. Rating the quality of evidence - imprecision. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1283-93. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011f
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Woodcock J, Brozek J, Helfand M, et al. GRADE guidelines: 7. Rating the quality of evidence - inconsistency. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1294-302. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011g
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Woodcock J, Brozek J, Helfand M, et al. GRADE guidelines: 8. Rating the quality of evidence - indirectness. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1303-10. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011h
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Sultan S, Glasziou P, Akl EA, Alonso-Coello P, et al. GRADE guidelines: 9. Rating up the quality of evidence. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1311-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Guyatt 2013a
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Sultan S, Brozek J, Glasziou P, Alonso-Coello P, et al. GRADE guidelines: 11. Making an overall rating of confidence in effect estimates for a single outcome and for all outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66(2):151-7. - PubMed
Guyatt 2013b
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Santesso N, Helfand M, Vist G, Kunz R, et al. GRADE guidelines: 12. Preparing summary of findings tables - binary outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66(2):158-72. - PubMed
Guyatt 2013c
-
- Guyatt GH, Thorlund K, Oxman AD, Walter SD, Patrick D, Furukawa TA, et al. GRADE guidelines: 13. Preparing summary of findings tables - continuous outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66(2):173-83. - PubMed
Guyatt 2013d
-
- Guyatt G, Andrews J, Oxman AD, Alderson P, Dahm P, Falck-Ytter Y, et al. GRADE guidelines: 15. Going from evidence to recommendations: the significance and presentation of recommendations. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66(7):719-25. - PubMed
Guyatt 2017
-
- Guyatt GH, Ebrahim S, Alonso-Coello P, Johnston BC, Mathioudakis AG, Briel M, et al. GRADE guidelines 17: assessing the risk of bias associated with missing participant outcome data in a body of evidence. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2017;87:14-22. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Han 2013
-
- Han YP, Kong M, Zheng S, Ren Y, Zhu L, Shi H, et al. Vitamin D in liver diseases: from mechanisms to clinical trials. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2013;28(Suppl 1):49-55. - PubMed
Hariri 2019
Harvey 2012
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(11):1539-58. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook/archive/v5.1.
Higgins 2021
-
- Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.2 (updated February 2021). Cochrane, 2021. Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook. - PMC - PubMed
Hilger 2014
-
- Hilger J, Friedel A, Herr R, Rausch T, Roos F, Wahl DA, et al. A systematic review of vitamin D status in populations worldwide. British Journal of Nutrition 2014;111(1):23-45. - PubMed
Hoan 2016
Holick 2007
-
- Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. New England Journal of Medicine 2007;357(3):266-81. - PubMed
Holick 2011
-
- Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Gordon CM, Hanley DA, Heaney RP, et al. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology 2011;96(7):1911-30. - PubMed
Hollis 1999
Hollis 2008
-
- Hollis BW. Measuring 25-hydroxyvitamin D in a clinical environment: challenges and needs. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2008;88(2):507S-10S. - PubMed
Hu 2019
ICH‐GCP 1997
-
- International Conference on Harmonisation Expert Working Group. International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline. Guideline for Good Clinical Practice CFR & ICH Guidelines. Vol. 1. Philadelphia: Barnett International/PAREXEL, 1997.
Ioannidis 2009
-
- Ioannidis JP. Adverse events in randomized trials: neglected, restricted, distorted, and silenced. Archives of Internal Medicine 2009;169(19):1737-9. - PubMed
IOM 2011
-
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. Washington, DC: National Academies Press, 2011. - PubMed
Iruzubieta 2014
Jakobsen 2014a
Jakobsen 2017
Jaruvongvanich 2017
-
- Jaruvongvanich V, Ahuja W, Sanguankeo A, Wijarnpreecha K, Upala S. Vitamin D and histologic severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Digestive and Liver Disease 2017;49(6):618-22. - PubMed
Johnson 2007
-
- Johnson RT, Dickersin K. Publication bias against negative results from clinical trials: three of the seven deadly sins. Nature Clinical Practice. Neurology 2007;3(11):590-1. - PubMed
Keum 2019
Keus 2010
Kim 2018
-
- Kim H-B, Myung S-K, Lee Y-J, Park B-J. Efficacy of vitamin D supplementation in combination with conventional antiviral therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics 2018;31(2):168-77. - PubMed
Kitson 2012
-
- Kitson MT, Roberts SK. D-livering the message: the importance of vitamin D status in chronic liver disease. Journal of Hepatology 2012;57(4):897-909. - PubMed
Kitson 2014
-
- Kitson MT, Sarrazin C, Toniutto P, Eslick GD, Roberts SK. Vitamin D level and sustained virologic response to interferon-based antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Hepatology 2014;61(6):1247-52. - PubMed
Kjaergard 2001
-
- Kjaergard LL, Villumsen J, Gluud C. Reported methodologic quality and discrepancies between large and small randomized trials in meta-analyses. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001;135(11):982-9. - PubMed
Konstantakis 2016
Kovesdy 2013
Kupferschmidt 2012
-
- Kupferschmidt K. Uncertain verdict as vitamin D goes on trial. Science 2012;337(6101):1476-8. - PubMed
Kwok 2013
-
- Kwok RM, Torres DM, Harrison SA. Vitamin D and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): is it more than just an association. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2013;58(3):1166-74. - PubMed
Lange 2013
Lesser 2007
Li 2013
-
- Li YJ, Tang YW, Shi YQ, Han S, Wang JB, Zhou XM, et al. Polymorphisms in the vitamin D receptor gene and risk of primary biliary cirrhosis: a meta-analysis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2013;29(4):706-15. - PubMed
Lim 2012
-
- Lim LY, Chalasani N. Vitamin D deficiency in patients with chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Current Gastroenterology Reports 2012;14(1):67-73. - PubMed
Lips 2004
-
- Lips P. Which circulating level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D is appropriate. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2004;89-90(1-5):611-4. - PubMed
Lips 2006
-
- Lips P. Vitamin D physiology. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology 2006;92(1):4-8. - PubMed
Lips 2010
-
- Lips P. Worldwide status of vitamin D nutrition. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2010;121(1-2):297-300. - PubMed
Lucas 2005
-
- Lucas JA, Bolland MJ, Grey AB, Ames RW, Mason BH, Horne AM, et al. Determinants of vitamin D status in older women living in a subtropical climate. Osteoporosis International 2005;16(12):1641-8. - PubMed
Lundh 2017
Luong 2012
Luong 2013a
Luong 2013b
Luxon 2011
-
- Luxon BA. Bone disorders in chronic liver diseases. Current Gastroenterology Reports 2011;13(1):40-8. - PubMed
Mahamid 2013
Malham 2011
Manson 2019
Mansour‐Ghanaei 2019
-
- Mansour-Ghanaei F, Pourmasoumi M, Hadi A, Ramezani-Jolfaie N, Joukar F. The efficacy of vitamin D supplementation against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a meta-analysis. Journal of Dietary Supplements 2019;17(4):467-85. - PubMed
Moher 1998
-
- Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, Cook DJ, Jadad A, Moher M, et al. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta-analysis. Lancet 1998;352(9128):609-13. - PubMed
Moher 2009
Mosannen 2017
-
- Mosannen Mozaffari H, Abbasi HA, Goshayeshi G, Esmaeelzadeh A, Bahari A, Mokhtarifar A, et al. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on chronic liver disease: systematic literature review. Reviews in Clinical Medicine 2017;4(1):14-9.
Mustafa 2013
-
- Mustafa RA, Santesso N, Brozek J, Akl EA, Walter SD, Norman G, et al. The GRADE approach is reproducible in assessing the quality of evidence of quantitative evidence syntheses. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66(7):736-42. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Nordic Trial Alliance 2015
-
- Nordic Trial Alliance Working Group on Transparency and Registration. Transparency and registration in clinical research in the Nordic countries. nta.nordforsk.org/projects/nta_transparency_report.pdf (accessed 6 November 2020).
Oliveira 2017
-
- Oliveira KD, Buss C, Tovo CV. Is there an association between vitamin D and liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Arquivos de Gastroenterologia 2017;54(1):57-9. - PubMed
Paternostro 2017
Peng 2020
Petta 2010
-
- Petta S, Cammà C, Scazzone C, Tripodo C, Di Marco V, Bono A, et al. Low vitamin D serum level is related to severe fibrosis and low responsiveness to interferon-based therapy in genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2010;51(4):1158-67. - PubMed
Putz‐Bankuti 2012
-
- Putz-Bankuti C, Pilz S, Stojakovic T, Scharnagl H, Pieber TR, Trauner M, et al. Association of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels with liver dysfunction and mortality in chronic liver disease. Liver International 2012;32(5):845-51. - PubMed
Reid 2014
-
- Reid IR, Bolland MJ, Grey A. Effects of vitamin D supplements on bone mineral density: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2014;383(9912):146-55. - PubMed
Review Manager 2020 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.4. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020.
SACN 2016
-
- Public Health England. SACN vitamin D and health report. www.gov.uk/government/publications/sacn-vitamin-d-and-health-report (accessed 17 July 2017).
Savović 2012a
-
- Savović J, Jones H, Altman D, Harris R, Jűni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomised controlled trials: combined analysis of meta-epidemiological studies. Health Technology Assessment 2012;16(35):1-82. - PubMed
Savović 2012b
-
- Savović J, Jones HE, Altman DG, Harris RJ, Jüni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomized, controlled trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 2012;157(6):429-38. - PubMed
Savović 2018a
-
- Savović J, Akl EA, Hróbjartsson A. Financial conflicts of interest in clinical research. Intensive Care Medicine 2018;44(10):1767-9. - PubMed
Savović 2018b
Sayiner 2016
-
- Sayiner M, Koenig A, Henry L, Younossi ZM. Epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in the United States and the rest of the world. Clinics in Liver Disease 2016;20(2):205-14. - PubMed
Schroll 2013
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273(5):408-12. - PubMed
Schünemann 2013
-
- Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A, editor(s). Handbook for grading the quality of evidence and the strength of recommendations using the GRADE approach (updated October 2013). GRADE Working Group, 2013. Available from gdt.guidelinedevelopment.org/app/handbook/handbook.html.
Scragg 2017
Scragg 2018
Sharifi 2019
-
- Sharifi N, Amani R. Vitamin D supplementation and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a critical and systematic review of clinical trials. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 2019;59(4):693-703. - PubMed
Siersma 2007
-
- Siersma V, Als-Nielsen B, Chen W, Hilden J, Gluud LL, Gluud C. Multivariable modelling for meta-epidemiological assessment of the association between trial quality and treatment effects estimated in randomized clinical trials. Statistics in Medicine 2007;26(14):2745-58. - PubMed
Sigma Stat 2003 [Computer program]
-
- Systat Software Inc. Sigma Stat 3.0. Systat Software Inc., 2003.
Skaaby 2014
-
- Skaaby T, Husemoen LL, Borglykke A, Jørgensen T, Thuesen BH, Pisinger C, et al. Vitamin D status, liver enzymes, and incident liver disease and mortality: a general population study. Endocrine 2014;47(1):213-20. - PubMed
Skaaby 2016
-
- Skaaby T, Husemoen LL, Thuesen BH, Pisinger C, Hannemann A, Jørgensen T. Longitudinal associations between lifestyle and vitamin D: a general population study with repeated vitamin D measurements. Endocrine 2016;51:342-50. - PubMed
StataCorp 2005 [Computer program]
-
- College Station, TX: StataCorp LP Intercooled Stata 8.2 for Windows. College Station, TX: StataCorp LP, 2005.
Stokes 2013
-
- Stokes CS, Volmer DA, Grünhage F, Lammert F. Vitamin D in chronic liver disease. Liver International 2013;33(3):338-52. - PubMed
Stokes 2014
-
- Stokes CS, Krawczyk M, Reichel C, Lammert F, Grünhage F. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with mortality in patients with advanced liver cirrhosis. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 2014;44(2):176-83. - PubMed
Storebø 2015
-
- Storebø OJ, Krogh HB, Ramstad E, Moreira-Maia CR, Holmskov M, Skoog M, et al. Methylphenidate for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: Cochrane systematic review with meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses of randomised clinical trials. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.) 2015;351:h5203. - PMC - PubMed
Storebø 2018
-
- Storebø OJ, Pedersen N, Ramstad E, Kielsholm ML, Nielsen SS, Krogh HB, et al. Methylphenidate for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents – assessment of adverse events in non-randomised studies. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2018, Issue 5. Art. No: CD012069. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012069.pub2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Tabrizi 2017
-
- Tabrizi R, Moosazadeh M, Lankarani KB, Akbari M, Heydari ST, Kolahdooz F, et al. The effects of vitamin D supplementation on metabolic profiles and liver function in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome 2017;11:S975-82. - PubMed
Thorlund 2009
-
- Thorlund K, Devereaux PJ, Wetterslev J, Guyatt G, Ioannidis JP, Thabane L, et al. Can trial sequential monitoring boundaries reduce spurious inferences from meta-analyses. International Journal of Epidemiology 2009;38(1):276-86. - PubMed
Thorlund 2011
Thorlund 2017
-
- Thorlund K, Engstrøm J, Wetterslev J, Brok J, Imberger G, Gluud C. User manual for Trial Sequential Analysis (TSA). ctu.dk/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/tsa_manual_ENG.pdf 2017 (accessed 2 September 2020).
Trépo 2013
-
- Trépo E, Ouziel R, Pradat P, Momozawa Y, Quertinmont E, Gervy C, et al. Marked 25-hydroxyvitamin D deficiency is associated with poor prognosis in patients with alcoholic liver disease. Journal of Hepatology 2013;59(2):344-50. - PubMed
TSA 2017 [Computer program]
-
- Copenhagen Trial Unit Trial Sequential Analysis. Copenhagen Trial Unit, Version 0.9.5.10 Beta. Copenhagen: Copenhagen Trial Unit, 2017. ctu.dk/tsa/downloads/.
Tsiaras 2011
-
- Tsiaras WG, Weinstock MA. Factors influencing vitamin D status. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 2011;91(2):115-24. - PubMed
Turner 2013
Van Schoor 2011
-
- Van Schoor NM, Lips P. Worldwide vitamin D status. Best Practice & Research. Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2011;25(4):671-80. - PubMed
Villar 2013
Wang 2013
-
- Wang JB, Abnet CC, Chen W, Dawsey SM, Fan JH, Yin LY, et al. Association between serum 25(OH) vitamin D, incident liver cancer and chronic liver disease mortality in the Linxian Nutrition Intervention Trials: a nested case-control study. British Journal of Cancer 2013;109(7):1997-2004. - PMC - PubMed
Wang 2015
Wesley Pike 2005
-
- Wesley Pike J, Shevde NK. The vitamin D receptor. In: Feldman D, Wesley Pike J, Glorieux FH, editors(s). Vitamin D. 2nd edition. Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press, 2005:167-91.
Wetterslev 2008
-
- Wetterslev J, Thorlund K, Brok J, Gluud C. Trial sequential analysis may establish when firm evidence is reached in cumulative meta-analysis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61(1):64-75. - PubMed
Wetterslev 2009
Wetterslev 2017
Williamson 2005
-
- Williamson PR, Gamble C, Altman DG, Hutton JL. Outcome selection bias in meta-analysis. Statistical Methods in Medical Research 2005;14(5):515-24. - PubMed
Wood 2008
Younossi 2016
-
- Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease - meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2016;64(1):73-84. - PubMed
Zhang 2019
Zittermann 2014
-
- Zittermann A, Ernst JB, Gummert JF, Börgermann J. Vitamin D supplementation, body weight and human serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D response: a systematic review. European Journal of Nutrition 2014;53(2):367-74. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Bjelakovic 2015
-
- Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Bjelakovic M, Gluud C. Vitamin D supplementation for chronic liver diseases in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 3. Art. No: CD011564. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011564] - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

