Neuroplasticity Caused by Peripheral Proprioceptive Deficits
- PMID: 34431830
- PMCID: PMC8677609
- DOI: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002775
Neuroplasticity Caused by Peripheral Proprioceptive Deficits
Abstract
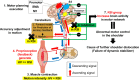
Purpose: Proprioceptive feedback is crucial for motor control and stabilization of the shoulder joint in everyday life and sports. Shoulder dislocation causes anatomical and proprioceptive feedback damage that contributes to subsequent dislocations. Previous recurrent anterior shoulder instability (RSI) studies did not investigate functional neuroplasticity related to proprioception of the injured shoulder. Thus, we aimed to study the differences in neuroplasticity related to motor control between patients with RSI and healthy individuals, using functional magnetic resonance imaging, and assess the effects of peripheral proprioceptive deficits due to RSI on CNS activity.
Methods: Using passive shoulder motion and voluntary shoulder muscles contraction tasks, we compared the CNS correlates of proprioceptive activity between patients having RSI (n = 13) and healthy controls (n = 12) to clarify RSI pathophysiology and the effects of RSI-related peripheral proprioceptive deficits on CNS activity.
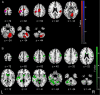
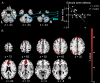
Results: Decreased proprioception-related brain activity indicated a deficient passive proprioception in patients with RSI (P < 0.05 family-wise error, cluster level). Proprioceptive afferent-related right cerebellar activity significantly negatively correlated with the extent of shoulder damage (P = 0.001, r = -0.79). Functional magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated abnormal motor control in the CNS during voluntary shoulder muscles contraction.
Conclusion: Our integrated analysis of peripheral anatomical information and brain activity during motion tasks can be used to investigate other orthopedic diseases.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American College of Sports Medicine.
Figures

References
-
- Bigliani LU, Kelkar R, Flatow EL, Pollock RG, Mow VC. Glenohumeral stability. Biomechanical properties of passive and active stabilizers. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;330:13–30. - PubMed
-
- Dodson CC, Cordasco FA. Anterior glenohumeral joint dislocations. Orthop Clin North Am. 2008;39(4):507–18. - PubMed
-
- Rowe CR, Patel D, Southmayd WW. The Bankart procedure: a long-term end-result study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978;60(1):1–16. - PubMed
-
- Burkhart SS, De Beer JF. Traumatic glenohumeral bone defects and their relationship to failure of arthroscopic Bankart repairs: significance of the inverted-pear glenoid and the humeral engaging Hill-Sachs lesion. Arthroscopy. 2000;16(7):677–94. - PubMed
-
- Milano G Grasso A Russo A, et al. . Analysis of risk factors for glenoid bone defect in anterior shoulder instability. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(9):1870–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

