Stanniocalcin-1 in the female reproductive system and pregnancy
- PMID: 34432025
- PMCID: PMC8542996
- DOI: 10.1093/humupd/dmab028
Stanniocalcin-1 in the female reproductive system and pregnancy
Abstract
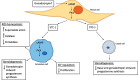
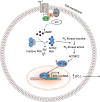
Background: Stanniocalcin-1 (STC-1) is a widely expressed glycoprotein hormone involved in a diverse spectrum of physiological and pathophysiological processes including angiogenesis, mineral homeostasis, cell proliferation, inflammation and apoptosis. Over the last 20 years, numerous studies have reported STC-1 expression within female reproductive tissues including the uterus, ovaries and placenta and implicated STC-1 in processes such as ovarian follicular development, blastocyst implantation, vascular remodelling in early pregnancy and placental development. Notably, dysregulation of STC-1 within reproductive tissues has been linked to the onset of severe reproductive disorders including endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, poor trophoblast invasion and placental perfusion in early pregnancy. Furthermore, significant changes in tissue expression and in maternal systemic concentration take place throughout pregnancy and further substantiate the vital role of this protein in reproductive health and disease.
Objective and rationale: Our aim is to provide a comprehensive overview of the existing literature, to summarise the expression profile and roles of STC-1 within the female reproductive system and its associated pathologies. We highlight the gaps in the current knowledge and suggest potential avenues for future research.
Search methods: Relevant studies were identified through searching the PubMed database using the following search terms: 'stanniocalcin-1', 'placenta', 'ovary', 'endometrium', 'pregnancy', 'reproduction', 'early gestation'. Only English language papers published between 1995 and 2020 were included.
Outcomes: This review provides compelling evidence of the vital function that STC-1 plays within the female reproductive system. The literature presented summarise the wide expression profile of STC-1 within female reproductive organs, as well as highlighting the putative roles of STC-1 in various functions in the reproductive system. Moreover, the observed link between altered STC-1 expression and the onset of various reproductive pathologies is presented, including those in pregnancy whose aetiology occurs in the first trimester. This summary emphasises the requirement for further studies on the mechanisms underlying the regulation of STC-1 expression and function.
Wider implications: STC-1 is a pleiotropic hormone involved in the regulation of a number of important biological functions needed to maintain female reproductive health. There is also growing evidence that dysregulation of STC-1 is implicated in common reproductive and obstetric disorders. Greater understanding of the physiology and biochemistry of STC-1 within the field may therefore identify possible targets for therapeutic intervention and/or diagnosis.
Keywords: stanniocalcin-1 / STC1 / reproduction / placenta / ovary / endometrium / uterus / pregnancy / decidualisation / implantation.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology.
Figures
References
-
- Abid N, Embola J, Tryfonos Z, Bercher J, Ashton SV, Khalil A, Thilaganathan B, Cartwright JE, Whitley GS.. Regulation of stanniocalcin‐1 secretion by BeWo cells and first trimester human placental tissue from normal pregnancies and those at increased risk of developing preeclampsia. FASEB J 2020;34:6086–6098. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allegra A, Marino A, Coffaro F, Lama A, Rizza G, Scaglione P, Sammartano F, Santoro A, Volpes A.. Is there a uniform basal endometrial gene expression profile during the implantation window in women who became pregnant in a subsequent ICSI cycle? Hum Reprod 2009;24:2549–2557. - PubMed
-
- Almeida M, Han L, O'brien CA, Kousteni S, Manolagas SC.. Classical genotropic versus kinase-initiated regulation of gene transcription by the estrogen receptor α. Endocrinology 2006;147:1986–1996. - PubMed

