Radio frequency plasma assisted surface modification of Fe3O4 nanoparticles using polyaniline/polypyrrole for bioimaging and magnetic hyperthermia applications
- PMID: 34432156
- PMCID: PMC8387263
- DOI: 10.1007/s10856-021-06563-1
Radio frequency plasma assisted surface modification of Fe3O4 nanoparticles using polyaniline/polypyrrole for bioimaging and magnetic hyperthermia applications
Abstract
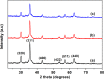
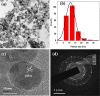
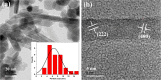
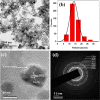
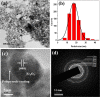
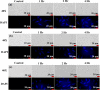
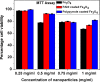
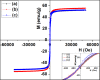
Surface modification of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles using polymers (polyaniline/polypyrrole) was done by radio frequency (r.f.) plasma polymerization technique and characterized by XRD, TEM, TG/DTA and VSM. Surface-passivated Fe3O4 nanoparticles with polymers were having spherical/rod-shaped structures with superparamagnetic properties. Broad visible photoluminescence emission bands were observed at 445 and 580 nm for polyaniline-coated Fe3O4 and at 488 nm for polypyrrole-coated Fe3O4. These samples exhibit good fluorescence emissions with L929 cellular assay and were non-toxic. Magnetic hyperthermia response of Fe3O4 and polymer (polyaniline/polypyrrole)-coated Fe3O4 was evaluated and all the samples exhibit hyperthermia activity in the range of 42-45 °C. Specific loss power (SLP) values of polyaniline and polypyrrole-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles (5 and 10 mg/ml) exhibit a controlled heat generation with an increase in the magnetic field.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bao Y, Sherwood JA, Sun Z. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as T1 contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. J Mater Chem C. 2018;6:1280–1290. doi: 10.1039/C7TC05854C. - DOI
-
- Abenojar EC, Wickramasinghe S, Bas-Concepcion J, Samia ACS. Structural effects on the magnetic hyperthermia properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog Nat Sci Mater. 2016;26:440–448. doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2016.09.004. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

