Meta-analytic connectivity modelling of deception-related brain regions
- PMID: 34432808
- PMCID: PMC8386837
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248909
Meta-analytic connectivity modelling of deception-related brain regions
Abstract
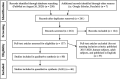
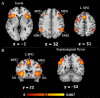
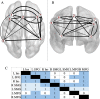
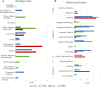
Brain-based deception research began only two decades ago and has since included a wide variety of contexts and response modalities for deception paradigms. Investigations of this sort serve to better our neuroscientific and legal knowledge of the ways in which individuals deceive others. To this end, we conducted activation likelihood estimation (ALE) and meta-analytic connectivity modelling (MACM) using BrainMap software to examine 45 task-based fMRI brain activation studies on deception. An activation likelihood estimation comparing activations during deceptive versus honest behavior revealed 7 significant peak activation clusters (bilateral insula, left superior frontal gyrus, bilateral supramarginal gyrus, and bilateral medial frontal gyrus). Meta-analytic connectivity modelling revealed an interconnected network amongst the 7 regions comprising both unidirectional and bidirectional connections. Together with subsequent behavioral and paradigm decoding, these findings implicate the supramarginal gyrus as a key component for the sociocognitive process of deception.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Merriam-Webster.com [Internet]. Deception. Merriam-Webster dictionary. [cited 2021 Jan 11]. Available from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/deception
-
- Zuckerman M, Koestner R, Driver R. Beliefs about cues associated with deception. J Nonverbal Behav. 1981Dec;6(2):105–114. 10.1007/BF00987286. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

