Global estimates of the implications of COVID-19-related preprimary school closures for children's instructional access, development, learning, and economic wellbeing
- PMID: 34432886
- PMCID: PMC8652862
- DOI: 10.1111/cdev.13658
Global estimates of the implications of COVID-19-related preprimary school closures for children's instructional access, development, learning, and economic wellbeing
Abstract
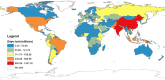
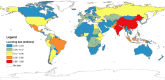
Observational data collected prior to the pandemic (between 2004 and 2019) were used to simulate the potential consequences of early childhood care and education (ECCE) service closures on the estimated 167 million preprimary-age children in 196 countries who lost ECCE access between March 2020 and February 2021. COVID-19-related ECCE disruptions were estimated to result in 19.01 billion person-days of ECCE instruction lost, 10.75 million additional children falling "off track" in their early development, 14.18 million grades of learning lost by adolescence, and a present discounted value of USD 308.02 billion of earnings lost in adulthood. Further burdens associated with ongoing closures were also forecasted. Projected developmental and learning losses were concentrated in low- and lower middle-income countries, likely exacerbating long-standing global inequities.
© 2021 The Authors. Child Development © 2021 Society for Research in Child Development.
Figures



References
-
- Azevedo, J. P. , Hasan, A. , Goldemberg, D. , Iqbal, S. A. , & Geven, K. (2020). Simulating the potential impacts of COVID‐19 school closures on schooling and learning outcomes. Policy Research Working Paper, 9284.
-
- Barnett, W. S. , & Nores, M. (2015). Investment and productivity arguments for ECCE. In Marope P. T. M., & Kaga Y. (Eds.), Investing against evidence: The global state of early childhood care and education (pp. 73–88). United Nations Educational, Science and Cultural Organization.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

