Exploring the efficacy and safety of polyene phosphatidylcholine for treatment of drug-induced liver injury using the Roussel Uclaf causality assessment method: a propensity score matching comparison
- PMID: 34433332
- PMCID: PMC8404657
- DOI: 10.1177/03000605211039810
Exploring the efficacy and safety of polyene phosphatidylcholine for treatment of drug-induced liver injury using the Roussel Uclaf causality assessment method: a propensity score matching comparison
Abstract
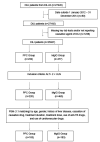
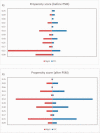
Objective In China, polyene phosphatidylcholine (PPC) is widely used to treat alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation associated with various liver diseases. Here, we assessed the efficacy and safety of PPC in treating drug-induced liver injury (DILI).Methods Data from a multicenter retrospective cohort study (DILI-R) were analyzed to compare PPC and magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate (MgIG) for treatment of DILI. We used the Roussel Uclaf causality assessment method (RUCAM) to evaluate patients with DILI. Patients with RUCAM scores ≥6 were included in the study, while those with RUCAM scores <6 were further evaluated by a panel of hepatologists. The primary outcome was the proportion of patients with ALT normalization at discharge. Propensity score matching was used to identify 183 matched pairs of patients (366 patients in total) from 25,927 patients with DILI.Results Among the DILI patients, 64 of 183 (34.97%) achieved normal ALT levels after treatment in both the PPC and the MgIG groups.Conclusion There were no significant differences in safety biomarkers including serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, white blood cells, platelets, hemoglobin, and albumin between patients treated with PPC or MgIG. The safety and efficacy of these two agents for treatment of DILI were comparable.
Keywords: Drug-induced liver injury; Roussel Uclaf causality assessment method; alanine aminotransferase; magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate; polyene phosphatidylcholine; propensity score matching.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Fan XF, Deng YQ, Ye L, et al.Effect of Xuezhikang capsule on serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hyperlipidemia. Chin J Integr Med. 2010; 16:119–123. - PubMed
-
- Li L, Zhang XJ, Lan Y, et al.Treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by Qianggan capsule. Chin J Integr Med. 2010; 16:23–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

