Portable, bedside, low-field magnetic resonance imaging for evaluation of intracerebral hemorrhage
- PMID: 34433813
- PMCID: PMC8387402
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-25441-6
Portable, bedside, low-field magnetic resonance imaging for evaluation of intracerebral hemorrhage
Abstract
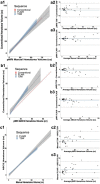
Radiological examination of the brain is a critical determinant of stroke care pathways. Accessible neuroimaging is essential to detect the presence of intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). Conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) operates at high magnetic field strength (1.5-3 T), which requires an access-controlled environment, rendering MRI often inaccessible. We demonstrate the use of a low-field MRI (0.064 T) for ICH evaluation. Patients were imaged using conventional neuroimaging (non-contrast computerized tomography (CT) or 1.5/3 T MRI) and portable MRI (pMRI) at Yale New Haven Hospital from July 2018 to November 2020. Two board-certified neuroradiologists evaluated a total of 144 pMRI examinations (56 ICH, 48 acute ischemic stroke, 40 healthy controls) and one ICH imaging core lab researcher reviewed the cases of disagreement. Raters correctly detected ICH in 45 of 56 cases (80.4% sensitivity, 95%CI: [0.68-0.90]). Blood-negative cases were correctly identified in 85 of 88 cases (96.6% specificity, 95%CI: [0.90-0.99]). Manually segmented hematoma volumes and ABC/2 estimated volumes on pMRI correlate with conventional imaging volumes (ICC = 0.955, p = 1.69e-30 and ICC = 0.875, p = 1.66e-8, respectively). Hematoma volumes measured on pMRI correlate with NIH stroke scale (NIHSS) and clinical outcome (mRS) at discharge for manual and ABC/2 volumes. Low-field pMRI may be useful in bringing advanced MRI technology to resource-limited settings.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
K.N.S. is the principal investigator. This study received support from the Collaborative Science Award from the American Heart Association (PIs: K.N.S., W.T.K., M.S.R.), National Institutes of Health Supplement Grant, and Hyperfine Research, Inc. research grant. W.T.K. receives grants from NIH and AHA; grants and personal fees from Biogen, Inc; grants and personal fees from NControl Therapeutics; has a patent pending that is licensed to NControl Therapeutics; holds equity in Woolsey Pharmaceuticals. M.S.R. is a co-founder of Hyperfine Research, Inc. J.R. is a co-founder of Hyperfine Research, Inc. E.B.W., L.S., and M.P. are research scientists and engineers at Hyperfine Research, Inc. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Powers WJ, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019;50:e344–e418. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.022606. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

