Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation activity in China 2019: a report from the Chinese Blood and Marrow Transplantation Registry Group
- PMID: 34433917
- PMCID: PMC8385702
- DOI: 10.1038/s41409-021-01431-6
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation activity in China 2019: a report from the Chinese Blood and Marrow Transplantation Registry Group
Abstract
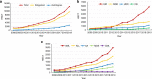
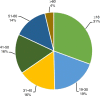
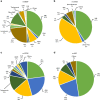
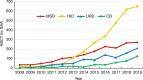
Between 2008 and 2019, 58,914 hematopoietic stem cell transplantations (HSCTs) were reported to the Chinese Blood and Marrow Transplantation Registry Group (CBMTRG) throughout China. In this report, we focus on 2019 data and describe current trends in HSCT in China. There was continued growth in transplant activity in China, with a rapid increase in haploidentical HSCT. In 2019, a total of 12,323 cases of HSCT were reported from 149 transplant teams, 78% (9597 cases) were allogeneic HSCTs. Haploidentical donor (HID) HSCT accounted for 60% (5771 cases) of allogeneic HSCT. The most common indications for allogeneic HSCT for malignant disease were acute myeloid leukemia (AML) (37%) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) (24%), and the largest proportion of non-malignant diseases comprised aplastic anemia (AA) (13%). Multiple stem cell source composed 70% of HID and 28% of MSD, which was typical in China. The BuCy based regimen (59%) was the most popular conditioning regimen for allogeneic HSCT, followed by the BuFlu based regimen (23%) and TBI-based regimen (12%). This survey clearly shows comprehensive information about the current state and recent trends for HSCT in China. Further efforts should be made to obtain detailed information.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Duarte RF, Labopin M, Bader P, Basak GW, Bonini C, Chabannon C, et al. Indications for haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for haematological diseases, solid tumours and immune disorders: current practice in Europe, 2019. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019;54:1525–52. doi: 10.1038/s41409-019-0516-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xu LP, Chen H, Chen J, Han MZ, Huang H, Kai YY, et al. The consensus on indications, conditioning regimen, and donor selection of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for hematological diseases in China-recommendations from the Chinese Society of Hematology. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11:33. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0564-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Worldwide Network for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. WBMT 2016 Survey Slides. 2020. https://www.wbmt.org/.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

