Computed Tomographic Image Processing and Reconstruction in the Diagnosis of Rare Osteochondroma
- PMID: 34434249
- PMCID: PMC8382554
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/2827556
Computed Tomographic Image Processing and Reconstruction in the Diagnosis of Rare Osteochondroma
Abstract
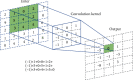
Objective: We applied computed tomography (CT) to explore the imaging manifestations of rare parts of osteochondroma. Based on the medical images, deblurring using a convolutional neural network (CNN), and three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of the images is performed in order to improve the image diagnosis.
Methods: Twelve cases of osteochondroma in rare locations confirmed by surgical pathology or clinical long-term dynamic observation were retrospectively analyzed using medical imaging and image reconstruction. There are 7 males and 5 females, with an average age of 43 years. CT examinations were performed in all cases. Image deblurring via the GAN model is performed followed by the 3D reconstruction of the higher quality images is implemented. A retrospective study was performed on the imaging manifestations of the above cases; the imaging characteristics were summarized.
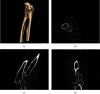
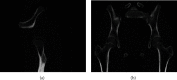
Results: The imaging features are the following lesions, including 4 cases of the proximal radius, 4 cases of the scapula, 2 cases of the pelvis, and 2 cases of the proximal ribs. The cartilage caps, cortex, and sternum were typical structures of the bone surface of the studied cases. In the continuous imaging features, calcification was visible in some cases, and no significant enhancement was seen in enhanced scans; there was no obvious direction of lesion growth. The image processing techniques that we performed are useful in enhancing the quality of the medical diagnosis.
Conclusions: Rare site osteochondroma has certain imaging features. In most cases, we can accurately diagnose rare site osteochondroma through these features via the image processing methods that are proposed in this paper.
Copyright © 2021 Ting Zhao and Hongyan Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

