Bilirubin is a specific marker for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis
- PMID: 34434270
- PMCID: PMC8353631
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.10490
Bilirubin is a specific marker for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis
Abstract
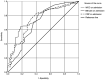
Total serum bilirubin and other biochemical parameters have been associated with acute appendicitis, mainly in complicated cases. The present study aimed to evaluate the role of biochemical parameters in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis, and to further investigate the role of bilirubin as a diagnostic marker irrespective of the severity of the pathology. All recorded cases of appendicectomies in a 1-year period in a single institution were reviewed. The median values of white cell count, C-reactive protein and total serum bilirubin on admission were associated with final histology, and their respective rates of abnormal and normal values were compared between patients who were proven to have negative histology and patients who were proven to have acute appendicitis. A total of 300 patients were studied. Median total serum bilirubin, white cell count and C-reactive protein on admission were significantly associated with acute appendicitis (P<0.001). Respective rates of normal and abnormal values were significantly associated with final histology (P<0.001). Total serum bilirubin demonstrated higher specificity (0.88) but lower sensitivity (0.26) and diagnostic accuracy (0.40) for acute appendicitis. In conclusion, total serum bilirubin on admission should be considered in the diagnostic workup to confirm rather than exclude appendicitis, without focusing on subgroups of specific severity of the disease. White cell count and C-reactive protein may also contribute to the diagnostic work-up, although with limited accuracy.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; acute appendicitis; bilirubin; histology; white cell count.
Copyright © 2020, Spandidos Publications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Slotboom T, Hamminga JT, Hofker HS, Heineman E, Haveman JW. Intraoperative motive for performing a laparoscopic appendectomy on a postoperative histological proven normal appendix. Scand J Surg. 2014;103:245–248. doi: 10.1177/1457496913519771. Apple Study Group A and Laparoscopic Evaluation. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eryigit V, Mahsanlar Y, Demirtas Y, Parlak I. The value of ultrasonography, leukocyte count and clinical results in diagnosis of acute appendicitis and the duration of stay of the patients in emergency department. Turk J Emerg Med. 2014;14:20–24. doi: 10.5505/1304.7361.2014.59251. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials