Spontaneous Subgaleal Hematoma in a Sickle Cell Disease Patient: A Case Report
- PMID: 34434360
- PMCID: PMC8383627
- DOI: 10.14740/jmc3433
Spontaneous Subgaleal Hematoma in a Sickle Cell Disease Patient: A Case Report
Abstract
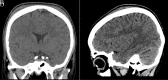
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is one of the most commonly inherited conditions on the Arabian Peninsula. We report a case of a 17-year-old boy, who had previously been diagnosed with SCD and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency and recently presented to our hospital with spontaneous subgaleal hematoma (SGH), which was managed conservatively. We also present a literature review on the topic of spontaneous intra- and/or extra-cranial bleeds.
Keywords: Extradural hematoma; Saudi Arabia; Sickle cell disease; Subgaleal hematoma.
Copyright 2020, Alqurashi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
There was no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous