Accurate, Traceable, and Verifiable Time Synchronization for World Financial Markets
- PMID: 34434634
- PMCID: PMC7339776
- DOI: 10.6028/jres.121.023
Accurate, Traceable, and Verifiable Time Synchronization for World Financial Markets
Abstract
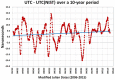
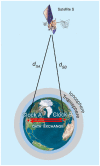
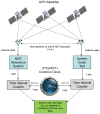
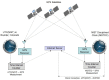
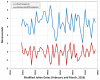
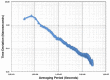
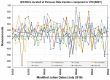
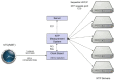
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), through a collaboration with Perseus, a global provider of telecommunication services, is providing accurate, traceable, and verifiable time synchronization to stock exchanges in the United States, Europe, and Asia. The paper describes why accurate time is necessary for fair and equitable financial markets and summarizes current and proposed future synchronization requirements in the financial sector. We discuss reference time sources and provide a technical overview of how NIST transfers time to data center hosted stock exchange. We also discuss how Perseus distributes NIST time to financial market customers and describes how the time is verified. Measurement data are presented, along with a discussion of measurement uncertainty.
Keywords: stock market; synchronization; time transfer; traceability.
Figures





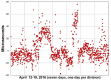

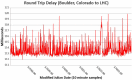
References
-
- Massimb MN. Phelps BD(1994) EElectronic Trading, Market Structure and Liquidity. Financial Analysts Journal 50(1):39–50. 10.2469/faj.v50.n1.39 - DOI
-
- Easley D, Lopez de Prado MM, O’Hara M (2011) The Microstructure of the “Flash Crash”: Flow Toxicity, Liquidity Crashes, and the Probability of Informed Trading. The Journal of Portfolio Management 37(2):118–128. http://ssrn.com/abstract=1695041
-
- Engel L, Hecht HR (1994) How to buy stocks (Little, Brown, Boston, MA: ) 8th Ed.
-
- Harris L (2003) Trading and exchanges: market microstructure for practitioners (Oxford University Press, Oxford; New York: ).
-
- Turner T (2007) A Beginner’s Guide To Day Trading Online (Adams Media, Avon, MA: ) 2nd Ed.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
