Mixture of Phlorotannin and Fucoidan from Ecklonia cava Prevents the Aβ-Induced Cognitive Decline with Mitochondrial and Cholinergic Activation
- PMID: 34436273
- PMCID: PMC8400198
- DOI: 10.3390/md19080434
Mixture of Phlorotannin and Fucoidan from Ecklonia cava Prevents the Aβ-Induced Cognitive Decline with Mitochondrial and Cholinergic Activation
Abstract
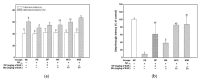
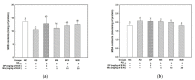
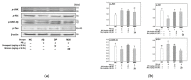
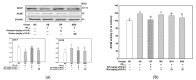
The anti-amnesic effect of a mixture (4:6 = phlorotannin:fucoidan from Ecklonia cava, P4F6) was evaluated on amyloid-beta peptide (Aβ)-induced cognitive deficit mice. The cognitive function was examined by Y-maze, passive avoidance, and Morris water maze tests, and the intake of the mixture (P4F6) showed an ameliorating effect on Aβ-induced learning and memory impairment. After the behavioral tests, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS) contents were confirmed in brain tissue, and in the results, the mixture (P4F6) attenuated Aβ-induced oxidative stress. In addition, mitochondrial activity was evaluated by mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) content, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), adenosine triphosphate (ATP) content, and mitochondria-mediated apoptotic signaling pathway, and the mixture (P4F6) enhanced mitochondrial function. Furthermore, the mixture (P4F6) effectively regulated tau hyperphosphorylation by regulating the protein kinase B (Akt) pathway, and promoted brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in brain tissue. Moreover, in the cholinergic system, the mixture (P4F6) ameliorated acetylcholine (ACh) content by regulating acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) expression in brain tissue. Based on these results, we suggest that this mixture of phlorotannin and fucoidan (P4F6) might be a substance for improving cognitive function by effectively regulating cognition-related molecules.
Keywords: Ecklonia cava; amyloid-beta; cholinergic function; cognition; fucoidan; mitochondrial function; phlorotannin; tau phosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Kang I.J., Jeon Y.E., Yin X.F., Nam J.S., You S.G., Hong M.S., Jang B.G., Kim M.J. Butanol extract of Ecklonia cava prevents production and aggregation of beta-amyloid, and reduces beta-amyloid mediated neuronal death. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011;49:2252–2259. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2011.06.023. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

