Contraindications to the Initiation of Veno-Venous ECMO for Severe Acute Respiratory Failure in Adults: A Systematic Review and Practical Approach Based on the Current Literature
- PMID: 34436348
- PMCID: PMC8400963
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes11080584
Contraindications to the Initiation of Veno-Venous ECMO for Severe Acute Respiratory Failure in Adults: A Systematic Review and Practical Approach Based on the Current Literature
Abstract
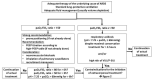
(1) Background: Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is increasingly used for acute respiratory failure with few absolute but many relative contraindications. The provider in charge often has a difficult time weighing indications and contraindications to anticipate if the patient will benefit from this treatment, a decision that often decides life and death for the patient. To assist in this process in coming to a good evidence-based decision, we reviewed the available literature. (2) Methods: We performed a systematic review through a literature search of the MEDLINE database of former and current absolute and relative contraindications to the initiation of ECMO treatment. (3) Results: The following relative and absolute contraindications were identified in the literature: absolute-refusal of the use of extracorporeal techniques by the patient, advanced stage of cancer, fatal intracerebral hemorrhage/cerebral herniation/intractable intracranial hypertension, irreversible destruction of the lung parenchyma without the possibility of transplantation, and contraindications to lung transplantation; relative-advanced age, immunosuppressed patients/pharmacological immunosuppression, injurious ventilator settings > 7 days, right-heart failure, hematologic malignancies, especially bone marrow transplantation and graft-versus-host disease, SAPS II score ≥ 60 points, SOFA score > 12 points, PRESERVE score ≥ 5 points, RESP score ≤ -2 points, PRESET score ≥ 6 points, and "do not attempt resuscitation" order (DN(A)R status). (4) Conclusions: We provide a simple-to-follow algorithm that incorporates absolute and relative contraindications to the initiation of ECMO treatment. This algorithm attempts to weigh pros and cons regarding the benefit for an individual patient and hopefully assists caregivers to make better, informed decisions.
Keywords: ARDS; ECMO; acute respiratory distress syndrome; contraindication; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; indication.
Conflict of interest statement
Lars-Olav Harnisch received noncash benefits for advanced trainings from CSL Behring, advisory fees from Baxter, and an unrestricted research grant from Sartorius AG Göttingen. Onnen Moerer received honoraria for lectures during workshops on hemodynamic monitoring, supported by Pulsion (Maquet Critical Care), and for two lectures during industrial sessions at national congresses (HillRom, HepaWash), as well as an unrestricted research grant from CSL Behring in 2015.
Figures


References
-
- Fichtner F., Moerer O., Laudi S., Weber-Carstens S., Nothacker M., Kaisers U., the Guideline Group on Mechanical Ventilation. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Acute Respiratory Insufficiency Mechanical Ventilation and Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygena tion in Acute Respiratory Insufficiency. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2018;115:840–847. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2018.0840. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fichtner F., Moerer O., Weber-Carstens S., Nothacker M., Kaisers U., Laudi S., Guideline G. Clinical Guideline for Treating Acute Respiratory Insufficiency with Invasive Ventilation and Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Evidence-Based Recommendations for Choosing Modes and Setting Parameters of Mechanical Ventilation. Respiration. 2019;98:357–372. doi: 10.1159/000502157. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zapol W.M., Snider M.T., Hill J.D., Fallat R.J., Bartlett R.H., Edmunds L.H., Morris A.H., Peirce E.C., 2nd, Thomas A.N., Proctor H.J., et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in severe acute respiratory failure. A randomized prospective study. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1979;242:2193–2196. doi: 10.1001/jama.1979.03300200023016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Peek G.J., Mugford M., Tiruvoipati R., Wilson A., Allen E., Thalanany M.M., Hibbert C.L., Truesdale A., Clemens F., Cooper N., et al. Efficacy and economic assessment of conventional ventilatory support versus extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe adult respiratory failure (CESAR): A multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;374:1351–1363. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61069-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

