Metformin Decreases 2-HG Production through the MYC-PHGDH Pathway in Suppressing Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation
- PMID: 34436421
- PMCID: PMC8402004
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo11080480
Metformin Decreases 2-HG Production through the MYC-PHGDH Pathway in Suppressing Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation
Abstract
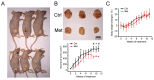
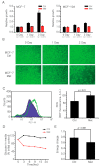
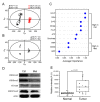
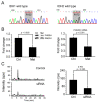
The biguanide drug metformin has been widely used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, and there is evidence supporting the anticancer effect of metformin despite some controversy. Here, we report the growth inhibitory activity of metformin in the breast cancer (MCF-7) cells, both in vitro and in vivo, and the associated metabolic changes. In particular, a decrease in a well-known oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) was discovered by a metabolomics approach. The decrease in 2-HG by metformin was accompanied by the reduction in histone methylation, consistent with the known tumorigenic mechanism of 2-HG. The relevance of 2-HG inhibition in breast cancer was also supported by a higher level of 2-HG in human breast cancer tissues. Genetic knockdown of PHGDH identified the PHGDH pathway as the producer of 2-HG in the MCF-7 cells that do not carry isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 (IDH1/IDH2) mutations, the conventional producer of 2-HG. We also showed that metformin's inhibitory effect on the PHGDH-2HG axis may occur through the regulation of the AMPK-MYC pathway. Overall, our results provide an explanation for the coherent pathway from complex I inhibition to epigenetic changes for metformin's anticancer effect.
Keywords: 2-HG; PHGDH; anticancer effect; metabolomics; metformin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chaudhury A., Duvoor C., Reddy Dendi V.S., Kraleti S., Chada A., Ravilla R., Marco A., Shekhawat N.S., Montales M.T., Kuriakose K., et al. Clinical Review of Antidiabetic Drugs: Implications for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management. Front. Endocrinol. 2017;8:6. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

