USP19 (ubiquitin specific peptidase 19) promotes TBK1 (TANK-binding kinase 1) degradation via chaperone-mediated autophagy
- PMID: 34436957
- PMCID: PMC9037486
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1963155
USP19 (ubiquitin specific peptidase 19) promotes TBK1 (TANK-binding kinase 1) degradation via chaperone-mediated autophagy
Abstract
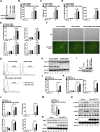
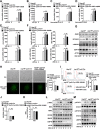
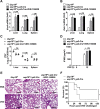
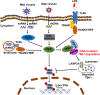
TBK1 (TANK-binding kinase 1) is an essential receptor protein required for the innate immune response, but the mechanisms underlying TBK1 stability, especially those regulated via autophagy, remain poorly understood. Here, we demonstrate that USP19 (ubiquitin specific peptidase 19) interacts with and promotes TBK1 lysosomal degradation via chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA). We observed that TBK1 had a canonical CMA motif, knocking down key proteins involved in CMA (HSPA8/HSC70 or LAMP2A) or inhibiting CMA-prevented USP19-mediated TBK1 degradation. Furthermore, USP19 deficiency in macrophages caused an elevation of TBK1 and the activation of the type-I interferon signaling pathway after vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) infection. Consistently, macrophage-specific usp19 knockout in mice resulted in attenuated VSV replication and resistance to VSV infection in vivo. Altogether, our results suggest that USP19 is a key regulator of TBK1 and uncovers a previously uncharacterized role for USP19 in CMA-mediated TBK1 degradation and infectious diseases.
Keywords: Antiviral immunity; autophagic degradation; hspa8/hsc70; lamp2a; type i interferon.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures





References
-
- Ktistakis NT, Tooze SA.. Digesting the expanding mechanisms of autophagy. Trends Cell Biol. 2016;26:624–635. - PubMed
-
- Shibutani ST, Saitoh T, Nowag H, et al. Autophagy and autophagy-related proteins in the immune system. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:1014–1024. - PubMed
-
- Mizushima N, Komatsu M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 2011;147:728–741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
