Investigation of Prognostic Value of Claudin-5, PSMA, and Ki67 Expression in Canine Splenic Hemangiosarcoma
- PMID: 34438863
- PMCID: PMC8388721
- DOI: 10.3390/ani11082406
Investigation of Prognostic Value of Claudin-5, PSMA, and Ki67 Expression in Canine Splenic Hemangiosarcoma
Abstract
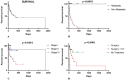
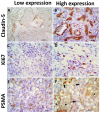
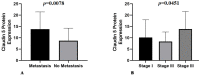
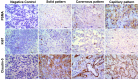
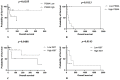
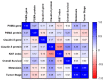
Splenic hemangiosarcoma (HSA) is a malignant tumor of endothelial cells that affects middle-aged and elderly dogs and is characterized by the formation of new blood vessels, commonly associated with necrotic and hemorrhagic areas. Despite its importance in veterinary medicine, few studies have identified markers with prognostic value for canine HSA. Thus, this study aimed to associate the clinicopathological findings (prostate-specific membrane antigen [PSMA], Claudin-5, and Ki67 gene and protein expression) with overall survival in HSA-affected patients. Fifty-three formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded canine splenic HSA samples, previously diagnosed by histopathological examination, were used in this study. Claudin-5, PSMA, and Ki67 protein expression levels were evaluated by immunohistochemistry, and gene expression was evaluated by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Claudin-5 protein overexpression was observed in patients with metastasis (p = 0.0078) and with stage III tumors compared to those with stage I and II tumors (p = 0.0451). In patients treated with surgery alone, low PSMA gene and protein expression (p = 0.05 and p = 0.0355, respectively) were associated with longer survival time. Longer survival time was observed in patients with a low Ki67 index (p = 0.0488). Our results indicate that Claudin-5 protein expression is associated with metastatic status, and PSMA gene and protein expression, and Ki67 index are associated with survival time.
Keywords: Ki67; canine spleen neoplasia; endothelial splenic neoplasia; proliferative index; prostate-specific membrane antigen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment of Canine Hemangiosarcoma: A Review Based on a Consensus Organized by the Brazilian Association of Veterinary Oncology, ABROVET.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 29;15(7):2025. doi: 10.3390/cancers15072025. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of prostate specific membrane antigen by canine hemangiosarcoma cells provides opportunity for the molecular detection of disease burdens within hemorrhagic body cavity effusions.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 2;14(1):e0210297. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210297. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30601866 Free PMC article.
-
Claudin-5 protein is a new differential marker for histopathological differential diagnosis of canine hemangiosarcoma.Histol Histopathol. 2009 Jul;24(7):801-13. doi: 10.14670/HH-24.801. Histol Histopathol. 2009. PMID: 19475526
-
More advantages in detecting bone and soft tissue metastases from prostate cancer using 18F-PSMA PET/CT.Hell J Nucl Med. 2019 Jan-Apr;22(1):6-9. doi: 10.1967/s002449910952. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Hell J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 30843003
-
Chromatin run-on sequencing analysis finds that ECM remodeling plays an important role in canine hemangiosarcoma pathogenesis.BMC Vet Res. 2020 Jun 22;16(1):206. doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02395-3. BMC Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 32571313 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Utility of Serum Ki-67 as a Marker for Malignancy in Dogs.Animals (Basel). 2022 May 14;12(10):1263. doi: 10.3390/ani12101263. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35625109 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating PSMA differential expression in canine uroepithelial carcinomas to aid disease-based stratification and guide therapeutic selection.BMC Vet Res. 2022 Dec 20;18(1):441. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03544-6. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 36539731 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment of Canine Hemangiosarcoma: A Review Based on a Consensus Organized by the Brazilian Association of Veterinary Oncology, ABROVET.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 29;15(7):2025. doi: 10.3390/cancers15072025. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neoplasia in pet guinea pigs: a retrospective analysis of 2,474 autopsy examinations.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2025 Jan;37(1):94-103. doi: 10.1177/10406387241288642. Epub 2024 Oct 14. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2025. PMID: 39397656 Free PMC article.
-
Hemangiosarcoma in dogs as a potential non-rodent animal model for drug discovery research of angiosarcoma in humans.Front Oncol. 2023 Dec 7;13:1250766. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1250766. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38130992 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sorenmo K.U., Baez J.L., Clifford C.A., Mauldin E., Overley B., Skorupski K. Efficacy & toxicity of a dose-intensified doxorubicin protocol in K9 HSA. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2004;18:209–213. - PubMed
-
- Mackin A., Henry C.J., Clifford C.A., Mackin A.J., Henry C.J. Treatment of Canine Hemangiosarcoma: 2000 and Beyond. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2000;4:479–485. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

