Time-Course Study of the Antibacterial Activity of an Amorphous SiOxCyHz Coating Certified for Food Contact
- PMID: 34438952
- PMCID: PMC8388733
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10080901
Time-Course Study of the Antibacterial Activity of an Amorphous SiOxCyHz Coating Certified for Food Contact
Abstract
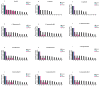
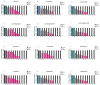
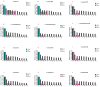
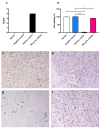
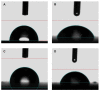
One of the most-used food contact materials is stainless steel (AISI 304L or AISI 316L), owing to its high mechanical strength, cleanability, and corrosion resistance. However, due to the presence of minimal crevices, stainless-steel is subject to microbial contamination with consequent significant reverb on health and industry costs due to the lack of effective reliability of sanitizing agents and procedures. In this study, we evaluated the noncytotoxic effect of an amorphous SiOxCyHz coating deposited on stainless-steel disks and performed a time-course evaluation for four Gram-negative bacteria and four Gram-positive bacteria. A low cytotoxicity of the SiOxCyHz coating was observed; moreover, except for some samples, a five-logarithm decrease was visible after 1 h on coated surfaces without any sanitizing treatment and inoculated with Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Conversely, a complete bacterial removal was observed after 30 s-1 min application of alcohol and already after 15 s under UVC irradiation against both bacterial groups. Moreover, coating deposition changed the wetting behaviors of treated samples, with contact angles increasing from 90.25° to 113.73°, realizing a transformation from hydrophilicity to hydrophobicity, with tremendous repercussions in various technological applications, including the food industry.
Keywords: SiOxCyHz coating; antibacterial activity; food contact material; hydrophobicity; stainless steel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 on Materials and Articles Intended to Come into Contact with Food and Repealing Directives 80/590/EEC and 89/109/EEC. [(accessed on 16 May 2021)];2004 Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:32004R193....
-
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 2023/2006 on Good Manufacturing Practice for Materials and Articles Intended to Come into Contact with Food. [(accessed on 17 May 2021)];2006 Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:32006R202...
-
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 333/2007 Laying down the Methods of Sampling and Analysis for the Official Control of the Levels of Lead, Cadmium, Mercury, Inorganic tin, 3-MCPD and Benzo(a)pyrene in Foodstuffs. [(accessed on 20 May 2021)];2007 Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:32007R033...
-
- Di Cerbo A., Mescola A., Rosace G., Stocchi R., Rossi G., Alessandrini A., Preziuso S., Scarano A., Rea S., Loschi A.R., et al. Antibacterial Effect of Stainless Steel Surfaces Treated with a Nanotechnological Coating Approved for Food Contact. Microorganisms. 2021;9:248. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9020248. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

