Pathological Roles and Clinical Usefulness of Periostin in Type 2 Inflammation and Pulmonary Fibrosis
- PMID: 34439751
- PMCID: PMC8391913
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11081084
Pathological Roles and Clinical Usefulness of Periostin in Type 2 Inflammation and Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
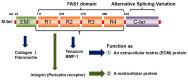
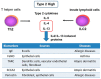
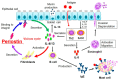
Periostin is known to be a useful biomarker for various diseases. In this article, we focus on allergic diseases and pulmonary fibrosis, for which we and others are now developing detection systems for periostin as a biomarker. Biomarker-based precision medicine in the management of type 2 inflammation and fibrotic diseases since heterogeneity is of utmost importance. Periostin expression is induced by type 2 cytokines (interleukin-4/-13) or transforming growth factor-β, and plays a vital role in the pathogenesis of allergic inflammation or interstitial lung disease, respectively, andits serum levels are correlated disease severity, prognosis and responsiveness to the treatment. We first summarise the importance of type 2 biomarker and then describe the pathological role of periostin in the development and progression of type 2 allergic inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis. In addition, then, we summarise the recent development of assay methods for periostin detection, and analyse the diseases in which periostin concentration is elevated in serum and local biological fluids and its usefulness as a biomarker. Furthermore, we describe recent findings of periostin as a biomarker in the use of biologics or anti-fibrotic therapy. Finally, we describe the factors that influence the change in periostin concentration under the healthy conditions.
Keywords: IL-13; biomarker; eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; periostin; type 2 inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Junya Ono, Masayuki Takai, Ayami Kamei and Yoshinori Azuma are employees of Shino-Test Corporation.
Figures
References
-
- Horiuchi K., Amizuka N., Takeshita S., Takamatsu H., Katsuura M., Ozawa H., Toyama Y., Bonewald L.F., Kudo A. Identification and characterization of a novel protein, periostin, with restricted expression to periosteum and periodontal ligament and increased expression by transforming growth factor beta. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1999;14:1239–1249. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1999.14.7.1239. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Takayama G., Arima K., Kanaji T., Toda S., Tanaka H., Shoji S., McKenzie A.N., Nagai H., Izuhara T.H.K. Periostin: A novel component of subepithelial fibrosis of bronchial asthma downstream of IL-4 and IL-13 signals. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006;118:98–104. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2006.02.046. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

