Bioinformatic Analysis of Two TOR (Target of Rapamycin)-Like Proteins Encoded by Entamoeba histolytica Revealed Structural Similarities with Functional Homologs
- PMID: 34440318
- PMCID: PMC8391992
- DOI: 10.3390/genes12081139
Bioinformatic Analysis of Two TOR (Target of Rapamycin)-Like Proteins Encoded by Entamoeba histolytica Revealed Structural Similarities with Functional Homologs
Abstract
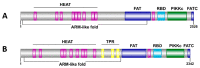
The target of rapamycin (TOR), also known as FKBP-rapamycin associated protein (FRAP), is a protein kinase belonging to the PIKK (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-related kinases) family. TOR kinases are involved in several signaling pathways that control cell growth and proliferation. Entamoeba histolytica, the protozoan parasite that causes human amoebiasis, contains two genes encoding TOR-like proteins: EhFRAP and EhTOR2. To assess their potential as drug targets to control the cell proliferation of E. histolytica, we studied the structural features of EhFRAP and EhTOR2 using a biocomputational approach. The overall results confirmed that both TOR amoebic homologs share structural similarities with functional TOR kinases, and show inherent abilities to form TORC complexes and participate in protein-protein interaction networks. To our knowledge, this study represents the first in silico characterization of the structure-function relationships of EhFRAP and EhTOR2.
Keywords: Entamoeba histolytica; FKBP-rapamycin associated protein; homology-based protein modeling; structure-function biocomputational analysis; target of rapamycin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

